Triangle Inequality
The triangle inequality states that the length of any side of a
triangle is less than or equal to the sum of the lengths of the other two
sides, with equality occurring only when the triangle degenerates to a
line. In ![]() , this becomes
, this becomes
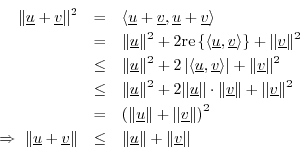
Next Section:
Triangle Difference Inequality
Previous Section:
Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality




















