The response of a state-space model Eq. (1.8) to initial
conditions, i.e., its initial state
(1.8) to initial
conditions, i.e., its initial state
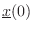 , is given by
, is given by
and the
complete response of a
linear system is given by the
sum of its
forced response (such as the
impulse response) and
its
initial-condition response.
In our force-driven mass example, with the external force set to zero,
we have, from Eq. (1.9) or Eq.
(1.9) or Eq. (1.11),
(1.11),
Thus, any initial
velocity 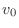
remains unchanged, as physically expected.
The initial position
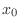
remains unchanged if the initial velocity is
zero. A nonzero initial velocity results in a linearly growing
position, as physically expected. This response to initial conditions
can be added to any forced response by superposition. The forced
response may be computed as the
convolution of the input driving force

with the
impulse response Eq.

(
1.11).
Next Section: State Space to Modal SynthesisPrevious Section: Impulse Response of State Space Models
![]() (1.8) to initial
conditions, i.e., its initial state
(1.8) to initial
conditions, i.e., its initial state
![]() , is given by
, is given by
![]() (1.9) or Eq.
(1.9) or Eq.![]() (1.11),
(1.11),
![$\displaystyle \left[\begin{array}{c} x_{n+1} \\ [2pt] v_{n+1} \end{array}\right...
...ght]
\eqsp \left[\begin{array}{c} x_0+v_0 n T \\ [2pt] v_0 \end{array}\right].
$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img286.png)




















