When the delay-line lengths need to be varied in real time, or
interactively in a GUI, it is convenient to choose each delay-line
length  as an integer power of a distinct prime number
as an integer power of a distinct prime number  [457]:
[457]:
where we call
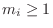
the ``multiplicity'' of the prime

. With
this choice, the delay-line lengths are always coprime (no factors in
common other than

), and yet we can lengthen or shorten each delay
line individually (by factors of

) without affecting the mutually
prime property.
Suppose we are initially given desired delay-line lengths  arranged in ascending order so that
arranged in ascending order so that
Then good prime-power approximations

can be expected using
the prime numbers in their natural order:
Since
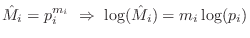
(for any
logarithmic base), an optimal (in some sense) choice of prime
multiplicity

is
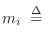
round
![$\displaystyle \left[\frac{\log(M_i)}{\log(p_i)}\right]
\isdefs \left\lfloor 0.5 + \frac{\log(M_i)}{\log(p_i)}\right\rfloor.
$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img808.png)
where

is the desired length in samples. That is,

can be
simply obtained by
rounding

to the
nearest integer (max 1). The prime-power delay-line length
approximation is then of course
and the multiplicative approximation error is bounded by
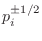
(when

).
This prime-power length scheme is used to keep 16 delay lines both
variable and mutually prime in Faust's reverb_designer.dsp
programming example (via the function prime_power_delays in
effect.lib).
Next Section: Conformal Map Interpretation of Damping SubstitutionPrevious Section: Mode Density Requirement
![]() as an integer power of a distinct prime number
as an integer power of a distinct prime number ![]() [457]:
[457]:
![]() arranged in ascending order so that
arranged in ascending order so that
![$\displaystyle \left[\frac{\log(M_i)}{\log(p_i)}\right]
\isdefs \left\lfloor 0.5 + \frac{\log(M_i)}{\log(p_i)}\right\rfloor.
$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img808.png)



















