Probability Distribution
Definition:
A probability distribution
![]() may be defined as a
non-negative real function of all possible outcomes of some random
event. The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes is
defined as 1, and probabilities can never be negative.
may be defined as a
non-negative real function of all possible outcomes of some random
event. The sum of the probabilities of all possible outcomes is
defined as 1, and probabilities can never be negative.
Example:
A coin toss has two outcomes, ``heads'' (H) or ``tails'' (T),
which are equally likely if the coin is ``fair''. In this case, the
probability distribution is
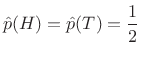 |
(C.1) |
where
Next Section:
Independent Events
Previous Section:
Time-Bandwidth Products Unbounded Above



















