Generate ideal QPSK..64QAM symbol error rates (reference result)
Calculates the symbol error rate of QPSK/16QAM/64QAM/256QAM/1024QAM modulation for additive white Gaussian noise
Output:
% ******************************************************
% Symbol error rate of Quadrature Amplitude Modulation
% ******************************************************
% uncoded, additive white Gaussian noise channel
% Implements [1] Figure 5.2-16 on a wider SNR range
% [1] John G. Proakis
% "Digital Communications"
% 4th edition, McGraw-Hill", 2001
% http://www.amazon.com/Digital-Communications-John-Proakis/dp/0072321113
% Note that different definitions are in common use:
% a) {symbol, bit} errors
% b) signal-to-noise ratio per {symbol, bit}
close all; clear all;
SNR_perSymbol_dB=[-3:0.1:42];
% definition: Below [1] 5.2-78
SNR_perSymbol=10.^(SNR_perSymbol_dB/10);
plotPerBitX=[]; plotY=[];
% number of constellation points (M-ary QAM)
for M=[4, 16, 64, 256, 1024]
% the energy of each symbol is used to transmit log2(M) bits
SNR_perBit=SNR_perSymbol/log2(M);
% [1] 5.2-78 argument of Q(...)
Qarg=sqrt(3/(M-1)*SNR_perSymbol);
% [1] 2.1-98
Q=1/2*erfc(Qarg/sqrt(2));
% [1] eq. 5.2-77
% probability of error for PAM per quadrature signal
PsqrtM=2*(1-1/sqrt(M))*Q;
% [1] eq. 5.2-79
PM=1-(1-PsqrtM).^2;
plotPerBitX=[plotPerBitX; 10*log10(SNR_perBit)];
plotY=[plotY; PM];
end
figure(1);
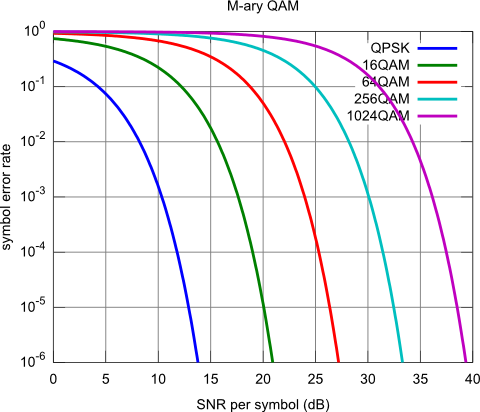
h = semilogy(SNR_perSymbol_dB', plotY'); grid on;
set(h, 'lineWidth', 3);
title('M-ary QAM'); xlabel('SNR per symbol (dB)'); ylabel('symbol error rate');
xlim([0, 40]); ylim([1e-6, 1]);
legend({'QPSK', '16QAM', '64QAM', '256QAM', '1024QAM'});
figure(2);
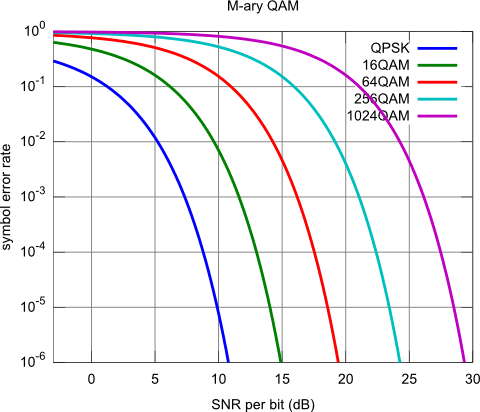
h = semilogy(plotPerBitX', plotY'); grid on; ylabel('symbol error rate');
set(h, 'lineWidth', 3);
title('M-ary QAM'); xlabel('SNR per bit (dB)');
xlim([-3, 30]); ylim([1e-6, 1]);
legend({'QPSK', '16QAM', '64QAM', '256QAM', '1024QAM'});


















