Normalized Fourier Transform Basis
The Fourier transform projects a continuous-time signal ![]() onto an
infinite set of continuous-time complex sinusoids
onto an
infinite set of continuous-time complex sinusoids
![]() ,
for
,
for
![]() . These sinusoids all have infinite
. These sinusoids all have infinite ![]() norm, but a simple normalization by
norm, but a simple normalization by
![]() can be chosen so
that the inverse Fourier transform has the desired form of a
superposition of projections:
can be chosen so
that the inverse Fourier transform has the desired form of a
superposition of projections:
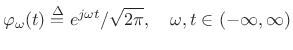 |
(12.113) |
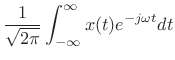 |
|||
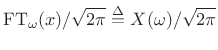 |
|||
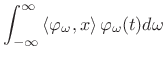 |
|||
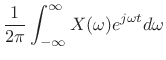 |
|||
Next Section:
Normalized DTFT Basis
Previous Section:
Normalized DFT Basis for



















