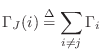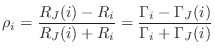Physical Derivation of Reflection Coefficient
Physically, the reflection coefficient seen at port ![]() is due to an
impedance step from
is due to an
impedance step from ![]() , that of the port interface, to a new
impedance consisting of the parallel combination of all other
port impedances meeting at the junction. Let
, that of the port interface, to a new
impedance consisting of the parallel combination of all other
port impedances meeting at the junction. Let
denote this parallel combination, in admittance form. Then we must have
Let's check this ``physical'' derivation against the formal definition
Eq.![]() (F.20) leading to
(F.20) leading to
![]() in Eq.
in Eq.![]() (F.22).
Toward this goal, let
(F.22).
Toward this goal, let
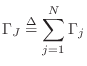
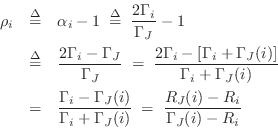
and the result is verified.
Next Section:
Reflection Free Port
Previous Section:
Reflection Coefficient, Parallel Case