Converting Propagation Distance to Delay Length
We may regard the delay-line memory itself as the fixed ``air'' which
propagates sound samples at a fixed speed ![]() (
(![]() meters per
second at
meters per
second at ![]() degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere). The input signal
degrees Celsius and 1 atmosphere). The input signal
![]() can be associated with a sound source, and the output signal
can be associated with a sound source, and the output signal
![]() (see Fig.2.1 on page
(see Fig.2.1 on page ![]() ) can be associated with
the listening point. If the listening point is
) can be associated with
the listening point. If the listening point is ![]() meters away from
the source, then the delay line length
meters away from
the source, then the delay line length ![]() needs to be
needs to be
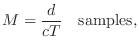
Next Section:
Spherical Waves from a Point Source
Previous Section:
Dispersive Traveling Waves




















