Two-Port Series Adaptor for Force Waves
Figure F.6a illustrates a generic two-port description of the series adaptor.
![\includegraphics[width=\twidth]{eps/lAdaptorSeries}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img4871.png) |
As discussed in §7.2, a series connection is characterized by a common velocity and forces which sum to zero at the junction:
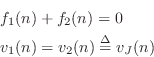
The derivation can proceed exactly as for the parallel junction in
§F.2.1, but with force and velocity interchanged, i.e.,
![]() , and with impedance and admittance interchanged,
i.e.,
, and with impedance and admittance interchanged,
i.e.,
![]() . In this way, we may take the
dual of Eq.
. In this way, we may take the
dual of Eq.![]() (F.14) to get
(F.14) to get
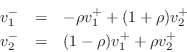
diagrammed in Fig.F.7. Converting back to force wave
variables via
![]() and
and
![]() , and noting
that
, and noting
that
![]() , we obtain, finally,
, we obtain, finally,
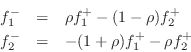
as diagrammed in Fig.F.6b. The one-multiply form is now
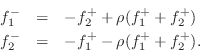
Next Section:
General Series Adaptor for Force Waves
Previous Section:
General Parallel Adaptor for Force Waves








![\includegraphics[scale=0.9]{eps/lscat_vel_series_renum}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img4881.png)











