Summary of Overlap-Add FFT Processing
Overlap-add FFT processors provide efficient implementations for FIR filters longer than 100 or so taps on single CPUs. Specifically, we ended up with:
![$\displaystyle y = \sum_{m=-\infty}^\infty \hbox{\sc Shift}_{mR} \left( \hbox{\sc DFT}_N^{-1} \left\{ H \cdot \hbox{\sc DFT}_N\left[\hbox{\sc Shift}_{-mR}(x)\cdot w \right]\right\}\right)$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/sasp2/img1446.png) |
(9.24) |
where
- (1)
- Extract the
 th length
th length  frame of data at time
frame of data at time 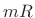 .
.
- (2)
- Shift it to the base time interval
![$ [0,M-1]$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/sasp2/img1448.png) (or
(or
![$ [-(M-1)/2,(M-1)/2]$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/sasp2/img1426.png) ).
).
- (3)
- Optionally apply a length
 analysis window
analysis window 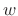 (causal or zero phase, as preferred). For simple LTI filtering,
the rectangular window is fine.
(causal or zero phase, as preferred). For simple LTI filtering,
the rectangular window is fine.
- (4)
- Zero-pad the windowed data out to the FFT size
 (a power of 2),
such that
(a power of 2),
such that
 , where
, where  is the FIR filter length.
is the FIR filter length.
- (5)
- Take the
 -point FFT.
-point FFT.
- (6)
- Apply the filter frequency-response
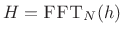 as a
windowing operation in the frequency domain.
as a
windowing operation in the frequency domain.
- (7)
- Take the
 -point inverse FFT.
-point inverse FFT.
- (8)
- Shift the origin of the
 -point result out to sample
-point result out to sample 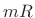 where it belongs.
where it belongs.
- (9)
- Sum into the output buffer containing the results from prior frames (OLA step).
A second condition is that the analysis window be COLA at the hop size used:
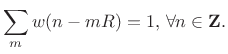 |
(9.25) |
Next Section:
Poisson Summation Formula
Previous Section:
Example of Overlap-Add Convolution



















