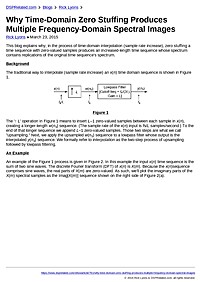
Why Time-Domain Zero Stuffing Produces Multiple Frequency-Domain Spectral Images
This blog explains why, in the process of time-domain interpolation (sample rate increase), zero stuffing a time sequence with zero-valued samples produces an increased-length time sequence whose spectrum contains replications of the original...

The Exponential Nature of the Complex Unit Circle
Introduction This is an article to hopefully give an understanding to Euler's magnificent equation: $$ e^{i\theta} = cos( \theta ) + i \cdot sin( \theta ) $$ This equation is usually proved using the Taylor series expansion for the given...

The Number 9, Not So Magic After All
This blog is not about signal processing. Rather, it discusses an interesting topic in number theory, the magic of the number 9. As such, this blog is for people who are charmed by the behavior and properties of numbers. For decades I've thought...

Signed serial-/parallel multiplication
Keywords: Binary signed multiplication implementation, RTL, Verilog, algorithm Summary A detailed discussion of bit-level trickstery in signed-signed multiplication Algorithm based on Wikipedia example Includes a Verilog implementation with...

Understanding and Preventing Overflow (I Had Too Much to Add Last Night)
Happy Thanksgiving! Maybe the memory of eating too much turkey is fresh in your mind. If so, this would be a good time to talk about overflow. In the world of floating-point arithmetic, overflow is possible but not particularly common. You can...
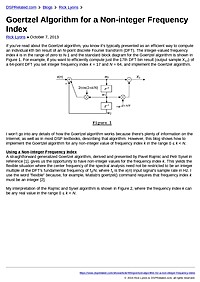
Goertzel Algorithm for a Non-integer Frequency Index
If you've read about the Goertzel algorithm, you know it's typically presented as an efficient way to compute an individual kth bin result of an N-point discrete Fourier transform (DFT). The integer-valued frequency index k is in the range of...

Adventures in Signal Processing with Python
Author’s note: This article was originally called Adventures in Signal Processing with Python (MATLAB? We don’t need no stinkin' MATLAB!) — the allusion to The Treasure of the Sierra Madre has been removed, in deference to being...

Python scipy.signal IIR Filtering: An Example
Introduction In the last posts I reviewed how to use the Python scipy.signal package to design digital infinite impulse response (IIR) filters, specifically, using the iirdesign function (IIR design I and IIR design...

Polyphase Filters and Filterbanks
ALONG CAME POLY Polyphase filtering is a computationally efficient structure for applying resampling and filtering to a signal. Most digital filters can be applied in a polyphase format, and it is also possible to create efficient resampling...
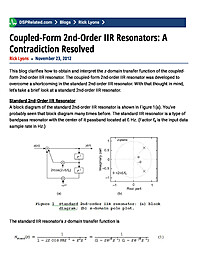
Coupled-Form 2nd-Order IIR Resonators: A Contradiction Resolved
This blog clarifies how to obtain and interpret the z-domain transfer function of the coupled-form 2nd-order IIR resonator. The coupled-form 2nd-order IIR resonator was developed to overcome a shortcoming in the standard 2nd-order IIR resonator....

Using Mason's Rule to Analyze DSP Networks
There have been times when I wanted to determine the z-domain transfer function of some discrete network, but my algebra skills failed me. Some time ago I learned Mason's Rule, which helped me solve my problems. If you're willing to learn the...
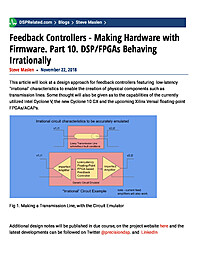
Feedback Controllers - Making Hardware with Firmware. Part 10. DSP/FPGAs Behaving Irrationally
This article will look at a design approach for feedback controllers featuring low-latency "irrational" characteristics to enable the creation of physical components such as transmission lines. Some thought will also be given as to...

Exponential Smoothing with a Wrinkle
Introduction This is an article to hopefully give a better understanding to the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) by providing a set of preprocessing filters to improve the resolution of the DFT. Because of the exponential nature of...

Simplest Calculation of Half-band Filter Coefficients
Half-band filters are lowpass FIR filters with cut-off frequency of one-quarter of sampling frequency fs and odd symmetry about fs/4 [1]*. And it so happens that almost half of the coefficients are zero. The passband and stopband bandwiths are equal, making these filters useful for decimation-by-2 and interpolation-by-2. Since the zero coefficients make them computationally efficient, these filters are ubiquitous in DSP systems. Here we will compute half-band coefficients using the window method. While the window method typically does not yield the fewest taps for a given performance, it is useful for learning about half-band filters. Efficient equiripple half-band filters can be designed using the Matlab function firhalfband [2].
IIR Bandpass Filters Using Cascaded Biquads
In an earlier post [1], we implemented lowpass IIR filters using a cascade of second-order IIR filters, or biquads. This post provides a Matlab function to do the same for Butterworth bandpass IIR filters. Compared to conventional implementations, bandpass filters based on biquads are less sensitive to coefficient quantization [2]. This becomes important when designing narrowband filters.

Ten Little Algorithms, Part 2: The Single-Pole Low-Pass Filter
Other articles in this series: Part 1: Russian Peasant Multiplication Part 2: The Single-Pole Low-Pass Filter Part 3: Welford’s Method (And Friends) Part 4: Topological Sort I’m writing this article in a room with a bunch of...

Should DSP Undergraduate Students Study Z-transform Regions of Convergence?
Not long ago I presented my 3-day DSP class to a group of engineers at Tektronix Inc. in Beaverton Oregon [1]. After I finished covering my material on IIR filters' z-plane pole locations and filter stability, one of the Tektronix engineers asked...

Use DPLL to Lock Digital Oscillator to 1PPS Signal
Introduction There are occasions where it is desirable to lock a digital oscillator to an external time reference such as the 1PPS (One Pulse Per Second) signal output from a GPS receiver. One approach would be to synchronize a fixed frequency...

An Astounding Digital Filter Design Application
I've recently encountered a digital filter design application that astonished me with its design flexibility, capability, and ease of use. The software is called the " ASN Filter Designer." After experimenting with a demo version of...

Round-robin or RTOS for my embedded system
First of all, I would like to introduce myself. I am Manuel Herrera. I am starting to write blogs about the situations that I have faced over the years of my career and discussed with colleagues.To begin, I would like to open a conversation...


















