Correlation Analysis
Correlation analysis applies only to stationary stochastic processes (§C.1.5).
Cross-Correlation
Definition: The cross-correlation of two signals ![]() and
and
![]() may be defined by
may be defined by
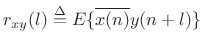 |
(C.24) |
I.e., it is the expected value (§C.1.6) of the lagged products in random signals
Cross-Power Spectral Density
The DTFT of the cross-correlation is called the cross-power spectral density, or ``cross-spectral density,'' ``cross-power spectrum,'' or even simply ``cross-spectrum.''
Autocorrelation
The cross-correlation of a signal with itself gives the autocorrelation function of that signal:
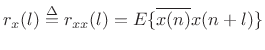 |
(C.25) |
Note that the autocorrelation function is Hermitian:
When
Sample Autocorrelation
See §6.4.
Power Spectral Density
The Fourier transform of the autocorrelation function ![]() is
called the power spectral density (PSD), or power
spectrum, and may be denoted
is
called the power spectral density (PSD), or power
spectrum, and may be denoted

When the signal
Sample Power Spectral Density
See §6.5.
Next Section:
White Noise
Previous Section:
Random Variables & Stochastic Processes



















