
Introduction of C Programming for DSP Applications
Appendix C of the book : Real-Time Digital Signal Processing: Implementations, Application and Experiments with the TMS320C55X

An Introduction To Compressive Sampling
This article surveys the theory of compressive sensing, also known as compressed sensing or CS, a novel sensing/sampling paradigm that goes against the common wisdom in data acquisition.

Introduction to Compressed Sensing
Chapter 1 of the book: "Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications".

C++ Tutorial
This tutorial is for those people who want to learn programming in C++ and do not necessarily have any previous knowledge of other programming languages. Of course any knowledge of other programming languages or any general computer skill can be useful to better understand this tutorial, although it is not essential. It is also suitable for those who need a little update on the new features the language has acquired from the latest standards. If you are familiar with the C language, you can take the first 3 parts of this tutorial as a review of concepts, since they mainly explain the C part of C++. There are slight differences in the C++ syntax for some C features, so I recommend you its reading anyway. The 4th part describes object-oriented programming. The 5th part mostly describes the new features introduced by ANSI-C++ standard.

Computing FFT Twiddle Factors
In this document are two algorithms showing how to compute the individual twiddle factors of an N-point decimation-in-frequency (DIF) and an N-point decimation-in-time (DIT) FFT.
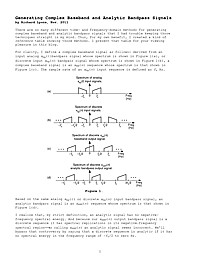
Generating Complex Baseband and Analytic Bandpass Signals
There are so many different time- and frequency-domain methods for generating complex baseband and analytic bandpass signals that I had trouble keeping those techniques straight in my mind. Thus, for my own benefit, I created a kind of reference table showing those methods. I present that table for your viewing pleasure in this document.

How Discrete Signal Interpolation Improves D/A Conversion
Earlier this year, for the Linear Audio magazine, published in the Netherlands whose subscribers are technically-skilled hi-fi audio enthusiasts, I wrote an article on the fundamentals of interpolation as it's used to improve the performance of analog-to-digital conversion. Perhaps that article will be of some value to the subscribers of dsprelated.com. Here's what I wrote: We encounter the process of digital-to-analog conversion every day—in telephone calls (land lines and cell phones), telephone answering machines, CD & DVD players, iPhones, digital television, MP3 players, digital radio, and even talking greeting cards. This material is a brief tutorial on how sample rate conversion improves the quality of digital-to-analog conversion.
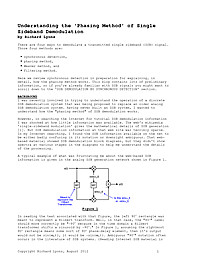
Understanding the 'Phasing Method' of Single Sideband Demodulation
There are four ways to demodulate a transmitted single sideband (SSB) signal. Those four methods are: synchronous detection, phasing method, Weaver method, and filtering method. Here we review synchronous detection in preparation for explaining, in detail, how the phasing method works. This blog contains lots of preliminary information, so if you're already familiar with SSB signals you might want to scroll down to the 'SSB DEMODULATION BY SYNCHRONOUS DETECTION' section.

Negative Group Delay
Dispersive linear systems with negative group delay have caused much confusion in the past. Some claim that they violate causality, others that they are the cause of superluminal tunneling. Can we really receive messages before they are sent? This article aims at pouring oil in the fire and causing yet more confusion :-).

Hybrid Floating Point Technique Yields 1.2 Gigasample Per Second 32 to 2048 point Floating Point FFT in a single FPGA
Hardware Digital Signal Processing, especially hardware targeted to FPGAs, has traditionally been done using fixed point arithmetic, mainly due to the high cost associated with implementing floating point arithmetic. That cost comes in the form of increased circuit complexity. The increase circuit complexity usually also degrades maximum clock performance. Certain applications demand the dynamic range offered by floating point hardware, and yet require the speeds and circuit density usually associated with fixed point hardware. The Fourier transform is one DSP building block that frequently requires floating point dynamic range. Textbook construction of a pipelined floating point FFT engine capable of continuous input entails dozens of floating point adders and multipliers. The complexity of those circuits quickly exceeds the resources available on a single FPGA. This paper describes a technique that is a hybrid of fixed point and floating point operations designed to significantly reduce the overhead for floating point. The results are illustrated with an FFT processor that performs 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024 and 2048 point Fourier transforms with IEEE single precision floating point inputs and outputs. The design achieves sufficient density to realize a continuous complex data rate of 1.2 Gigasamples per second data throughput using a single Virtex4-SX55-10 device.

A Nonlinear Stein Based Estimator for Multichannel Image Denoising
The use of multicomponent images has become widespread with the improvement of multisensor systems having increased spatial and spectral resolutions. However, the observed images are often corrupted by an additive Gaussian noise. In this paper, we are interested in multichannel image denoising based on a multiscale representation of the images. A multivariate statistical approach is adopted to take into account both the spatial and the inter-component correlations existing between the different wavelet subbands. More precisely, we propose a new parametric nonlinear estimator which generalizes many reported denoising methods. The derivation of the optimal parameters is achieved by applying Stein’s principle in the multivariate case. Experiments performed on multispectral remote sensing images clearly indicate that our method outperforms conventional wavelet denoising techniques.
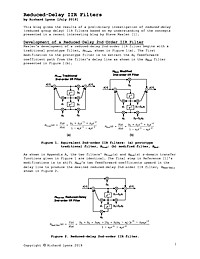
Reduced-Delay IIR Filters
This document describes a straightforward method to significantly reduce the number of necessary multiplies per input sample of traditional IIR lowpass and highpass digital filters.

Using the DFT as a Filter: Correcting a Misconception
I have read, in some of the literature of DSP, that when the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is used as a filter the process of performing a DFT causes an input signal's spectrum to be frequency translated down to zero Hz (DC). I can understand why someone might say that, but I challenge that statement as being incorrect. Here are my thoughts.

Region based Active Contour Segmentation
In this paper, we propose a natural framework that allows any region-based segmentation energy to be re-formulated in a local way. We consider local rather than global image statistics and evolve a contour based on local information. Localized contours are capable of segmenting objects with heterogeneous feature profiles that would be difficult to capture correctly using a standard global method. The presented technique is versatile enough to be used with any global region-based active contour energy and instill in it the benefits of localization. We describe this framework and demonstrate the localization of three well-known energies in order to illustrate how our framework can be applied to any energy. We then compare each localized energy to its global counterpart to show the improvements that can be achieved. Next, an in-depth study of the behaviors of these energies in response to the degree of localization is given. Finally, we show results on challenging images to illustrate the robust and accurate segmentations that are possible with this new class of active contour models.

Wavelet Denoising for TDR Dynamic Range Improvement
A technique is presented for removing large amounts of noise present in time-domain-reflectometry (TDR) waveforms to increase the dynamic range of TDR waveforms and TDR based s-parameter measurements.

Algorithm Adaptation and Optimization of a Novel DSP Vector Co-processor
The Division of Computer Engineering at Linköping's university is currently researching the possibility to create a highly parallel DSP platform, that can keep up with the computational needs of upcoming standards for various applications, at low cost and low power consumption. The architecture is called ePUMA and it combines a general RISC DSP master processor with eight SIMD co-processors on a single chip. The master processor will act as the main processor for general tasks and execution control, while the co-processors will accelerate computing intensive and parallel DSP kernels.This thesis investigates the performance potential of the co-processors by implementing matrix algebra kernels for QR decomposition, LU decomposition, matrix determinant and matrix inverse, that run on a single co-processor. The kernels will then be evaluated to find possible problems with the co-processors' microarchitecture and suggest solutions to the problems that might exist. The evaluation shows that the performance potential is very good, but a few problems have been identified, that causes significant overhead in the kernels. Pipeline mismatches, that occurs due to different pipeline lengths for different instructions, causes pipeline hazards and the current solution to this, doesn't allow effective use of the pipeline. In some cases, the single port memories will cause bottlenecks, but the thesis suggests that the situation could be greatly improved by using buffered memory write-back. Also, the lack of register forwarding makes kernels with many data dependencies run unnecessarily slow.

Digital Signal Processing Maths
Modern digital signal processing makes use of a variety of mathematical techniques. These techniques are used to design and understand efficient filters for data processing and control.

A DSP Implementation of OFDM Acoustic Modem
The success of multicarrier modulation in the form of OFDM in radio channels illuminates a path one could take towards high-rate underwater acoustic communications, and recently there are intensive investigations on underwater OFDM. In this paper, we implement the acoustic OFDM transmitter and receiver design of [4, 5] on a TMS320C6713 DSP board. We analyze the workload and identify the most time-consuming operations. Based on the workload analysis, we tune the algorithms and optimize the code to substantially reduce the synchronization time to 0.2 seconds and the processing time of one OFDM block to 1.7 seconds on a DSP processor at 225 MHz. This experimentation provides guidelines on our future work to reduce the per-block processing time to be less than the block duration of 0.23 seconds for real time operations.




















