
Sum of Two Equal-Frequency Sinusoids
The sum of two equal-frequency real sinusoids is itself a single real sinusoid. However, the exact equations for all the various forms of that single equivalent sinusoid are difficult to find in the signal processing literature. Here we provide those equations.

Using the DFT as a Filter: Correcting a Misconception
I have read, in some of the literature of DSP, that when the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is used as a filter the process of performing a DFT causes an input signal's spectrum to be frequency translated down to zero Hz (DC). I can understand why someone might say that, but I challenge that statement as being incorrect. Here are my thoughts.

Negative Group Delay
Dispersive linear systems with negative group delay have caused much confusion in the past. Some claim that they violate causality, others that they are the cause of superluminal tunneling. Can we really receive messages before they are sent? This article aims at pouring oil in the fire and causing yet more confusion :-).

Implementing Simultaneous Digital Differentiation, Hilbert Transformation, and Half-Band Filtering
Recently I've been thinking about digital differentiator and Hilbert transformer implementations and I've developed a processing scheme that may be of interest to the readers here on dsprelated.com.
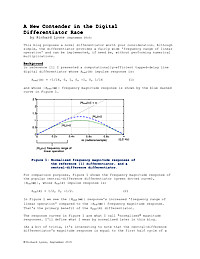
A New Contender in the Digital Differentiator Race
This blog proposes a novel differentiator worth your consideration. Although simple, the differentiator provides a fairly wide 'frequency range of linear operation' and can be implemented, if need be, without performing numerical multiplications.
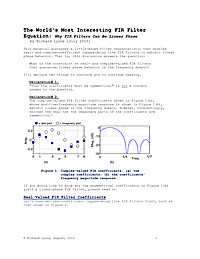
The World's Most Interesting FIR Filter Equation: Why FIR Filters Can Be Linear Phase
This article discusses a little-known filter characteristic that enables real- and complex-coefficient tapped-delay line FIR filters to exhibit linear phase behavior. That is, this article answers the question: What is the constraint on real- and complex-valued FIR filters that guarantee linear phase behavior in the frequency domain?
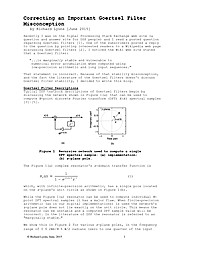
Correcting an Important Goertzel Filter Misconception
Correcting an Important Goertzel Filter Misconception

Complex Down-Conversion Amplitude Loss
This article illustrates the signal amplitude loss inherent in a traditional complex down-conversion system. (In the literature of signal processing, complex down-conversion is also called "quadrature demodulation.")
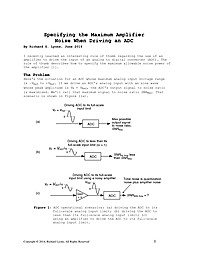
Specifying the Maximum Amplifier Noise When Driving an ADC
I recently learned an interesting rule of thumb regarding the use of an amplifier to drive the input of an analog to digital converter (ADC). The rule of thumb describes how to specify the maximum allowable noise power of the amplifier.

Specifying the Maximum Amplifier Noise When Driving an ADC
I recently learned an interesting rule of thumb regarding the use of an amplifier to drive the input of an analog to digital converter (ADC). The rule of thumb describes how to specify the maximum allowable noise power of the amplifier.

How Discrete Signal Interpolation Improves D/A Conversion
Earlier this year, for the Linear Audio magazine, published in the Netherlands whose subscribers are technically-skilled hi-fi audio enthusiasts, I wrote an article on the fundamentals of interpolation as it's used to improve the performance of analog-to-digital conversion. Perhaps that article will be of some value to the subscribers of dsprelated.com. Here's what I wrote: We encounter the process of digital-to-analog conversion every day—in telephone calls (land lines and cell phones), telephone answering machines, CD & DVD players, iPhones, digital television, MP3 players, digital radio, and even talking greeting cards. This material is a brief tutorial on how sample rate conversion improves the quality of digital-to-analog conversion.

Fixed-Point Arithmetic: An Introduction
This document presents definitions of signed and unsigned fixed-point binary number representations and develops basic rules and guidelines for the manipulation of these number representations using the common arithmetic and logical operations found in fixed-point DSPs and hardware components.

Hilbert Transform and Applications
Section 1: reviews the mathematical definition of Hilbert transform and various ways to calculate it.
Sections 2 and 3: review applications of Hilbert transform in two major areas: Signal processing and system identification.
Section 4: concludes with remarks on the historical development of Hilbert transform

Voice Activity Detection. Fundamentals and Speech Recognition System Robustness
An important drawback affecting most of the speech processing systems is the environmental noise and its harmful effect on the system performance. Examples of such systems are the new wireless communications voice services or digital hearing aid devices. In speech recognition, there are still technical barriers inhibiting such systems from meeting the demands of modern applications. Numerous noise reduction techniques have been developed to palliate the effect of the noise on the system performance and often require an estimate of the noise statistics obtained by means of a precise voice activity detector (VAD). Speech/non-speech detection is an unsolved problem in speech processing and affects numerous applications including robust speech recognition, discontinuous transmission, real-time speech transmission on the Internet or combined noise reduction and echo cancellation schemes in the context of telephony. The speech/non-speech classification task is not as trivial as it appears, and most of the VAD algorithms fail when the level of background noise increases. During the last decade, numerous researchers have developed different strategies for detecting speech on a noisy signal and have evaluated the influence of the VAD effectiveness on the performance of speech processing systems. Most of the approaches have focussed on the development of robust algorithms with special attention being paid to the derivation and study of noise robust features and decision rules. The different VAD methods include those based on energy thresholds, pitch detection, spectrum analysis, zero-crossing rate, periodicity measure, higher order statistics in the LPC residual domain or combinations of different features. This chapter shows a comprehensive approximation to the main challenges in voice activity detection, the different solutions that have been reported in a complete review of the state of the art and the evaluation frameworks that are normally used. The application of VADs for speech coding, speech enhancement and robust speech recognition systems is shown and discussed. Three different VAD methods are described and compared to standardized and recently reported strategies by assessing the speech/non-speech discrimination accuracy and the robustness of speech recognition systems.

Multirate Systems and Filter Banks
During the last two decades, multirate filter banks have found various applications in many different areas, such as speech coding, scrambling, adaptive signal processing, image compression, signal and image processing applications as well as transmission of several signals through the same channel. The main idea of using multirate filter banks is the ability of the system to separate in the frequency domain the signal under consideration into two or more signals or to compose two or more different signals into a single signal.

A Review of Physical and Perceptual Feature Extraction Techniques for Speech, Music and Environmental Sounds
Endowing machines with sensing capabilities similar to those of humans is a prevalent quest in engineering and computer science. In the pursuit of making computers sense their surroundings, a huge effort has been conducted to allow machines and computers to acquire, process, analyze and understand their environment in a human-like way. Focusing on the sense of hearing, the ability of computers to sense their acoustic environment as humans do goes by the name of machine hearing. To achieve this ambitious aim, the representation of the audio signal is of paramount importance. In this paper, we present an up-to-date review of the most relevant audio feature extraction techniques developed to analyze the most usual audio signals: speech, music and environmental sounds. Besides revisiting classic approaches for completeness, we include the latest advances in the field based on new domains of analysis together with novel bio-inspired proposals. These approaches are described following a taxonomy that organizes them according to their physical or perceptual basis, being subsequently divided depending on the domain of computation (time, frequency, wavelet, image-based, cepstral, or other domains). The description of the approaches is accompanied with recent examples of their application to machine hearing related problems.

Sum of Two Equal-Frequency Sinusoids
The sum of two equal-frequency real sinusoids is itself a single real sinusoid. However, the exact equations for all the various forms of that single equivalent sinusoid are difficult to find in the signal processing literature. Here we provide those equations.

Peak-to-Average Power Ratio and CCDF
Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) is often used to characterize digitally modulated signals. One example application is setting the level of the signal in a digital modulator. Knowing PAPR allows setting the average power to a level that is just low enough to minimize clipping.




















