
An Introduction To Compressive Sampling
This article surveys the theory of compressive sensing, also known as compressed sensing or CS, a novel sensing/sampling paradigm that goes against the common wisdom in data acquisition.

Introduction to Compressed Sensing
Chapter 1 of the book: "Compressed Sensing: Theory and Applications".

Introduction to Real-Time Digital Signal Processing
Chapter 1 of the book: Real-Time Digital Signal Processing: Fundamentals, Implementations and Applications, 3rd Edition

A Pragmatic Introduction to Signal Processing
An illustrated essay with software available for free download.

Introduction to Signal Processing
This book provides an applications-oriented introduction to digital signal processing written primarily for electrical engineering undergraduates. Practicing engineers and graduate students may also find it useful as a first text on the subject.

C++ Tutorial
This tutorial is for those people who want to learn programming in C++ and do not necessarily have any previous knowledge of other programming languages. Of course any knowledge of other programming languages or any general computer skill can be useful to better understand this tutorial, although it is not essential. It is also suitable for those who need a little update on the new features the language has acquired from the latest standards. If you are familiar with the C language, you can take the first 3 parts of this tutorial as a review of concepts, since they mainly explain the C part of C++. There are slight differences in the C++ syntax for some C features, so I recommend you its reading anyway. The 4th part describes object-oriented programming. The 5th part mostly describes the new features introduced by ANSI-C++ standard.

Computing FFT Twiddle Factors
In this document are two algorithms showing how to compute the individual twiddle factors of an N-point decimation-in-frequency (DIF) and an N-point decimation-in-time (DIT) FFT.
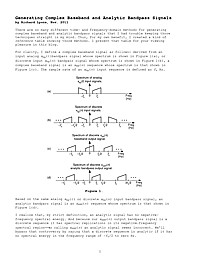
Generating Complex Baseband and Analytic Bandpass Signals
There are so many different time- and frequency-domain methods for generating complex baseband and analytic bandpass signals that I had trouble keeping those techniques straight in my mind. Thus, for my own benefit, I created a kind of reference table showing those methods. I present that table for your viewing pleasure in this document.

Implementation of Uncoordinated Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum using Software Defined Radios
One of the major threats to wireless communications is jamming. Many anti-jamming techniques have been presented in the past. However most of them are based on the precondition that the communicating devices have a pre-shared secret that can be used to synchronize the anti-jamming scheme. E.g. for frequency hopping the secret could be used to derive the hopping sequence and for direct sequence spread spectrum the secret is used to derive the spreading codes. But how can the devices bootstrap a jamming-resistant communication without having a pre-shared secret? Christina Popper and Mario Strasser propose as scheme for Uncoordinated Frequency Hopping (UFH) and Uncoordinated Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (UDSSS) in their papers [1] and [2] respectively. The goal of my project was an implementation of Uncoordinated Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (UDSSS) using Software De ned Radios. The First version should serve as an easy to use and extendable proof of conceptfor the proposed scheme.

Algorithms and tools for automatic generation of DSP hardware structures
The increased complexity of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) algorithms demands for the development of more complex and more efficient hardware structures. The work presented herein describes the core components for the development of a tool capable of automatic generation of efficient hardware structures, therefore facilitating developers work. It comprises algorithms and techniques for i) balancing the paths in a graph, ii) scheduling of operations to functional units, iii) allocating registers and iv) generating the VHDL code. Results show that the developed techniques are capable of generating the hardware structure of typical DSP algorithms represented in data-flow graphs with over 2,000 nodes in around 200 ms, scaling to 80,000 nodes in about 214 s. Within the developed techniques, solving the scheduling problem is one of the most complex tasks: it is a NP-complete problem and directly influences the number of functional units and registers required. Therefore, experimental analysis was made on scheduling algorithms for time-constrained problems. Results show that simple list-based algorithms are more efficient in large problems than more complex algorithms: they run faster and tend to require less functional units.
Audio Time-Scale Modification
Audio time-scale modification is an audio effect that alters the duration of an audio signal without affecting its perceived local pitch and timbral characteristics. There are two broad categories of time-scale modification algorithms, time-domain and frequency-domain. The computationally efficient time-domain techniques produce high quality results for single pitched signals such as speech, but do not cope well with more complex signals such as polyphonic music. The less efficient frequencydomain techniques have proven to be more robust and produce high quality results for a variety of signals; however they introduce a reverberant artefact into the output. This dissertation focuses on incorporating aspects of time-domain techniques into frequency-domain techniques in an attempt to reduce the presence of the reverberant artefact and improve upon computational demands. From a review of prior work it was found that there are a number of time-domain algorithms available and that the choice of algorithm parameters varies considerably in the literature. This finding prompted an investigation into the effects of the choice of parameters and a comparison of the various techniques employed in terms of computational requirements and output quality. The investigation resulted in the derivation of an efficient and flexible parameter set for use within time-domain implementations. Of the available frequency-domain approaches the phase vocoder and timedomain/ subband techniques offer an efficiency and robustness advantage over sinusoidal modelling and iterative phase update techniques, and as such were identified as suitable candidates for the provision of a framework for further investigation. Following from this observation, improvements in the quality produced by time-domain/subband techniques are realised through the use of a bark based subband partitioning approach and effective subband synchronisation techniques. In addition, computational and output quality improvements within a phase vocoder implementation are achieved by taking advantage of a certain level of flexibility in the choice of phase within such an implementation. The phase flexibility established is used to push or pull phase values into a phase coherent state. Further improvements are realised by incorporating features of time-domain algorithms into the system in order to provide a ‘good’ initial set of phase estimates; the transition to ‘perfect’ phase coherence is significantly reduced through this scheme, thereby improving the overall output quality produced. The result is a robust and efficient time-scale modification algorithm which draws upon various aspects of a number of general approaches to time-scale modification.

Multirate Systems and Filter Banks
During the last two decades, multirate filter banks have found various applications in many different areas, such as speech coding, scrambling, adaptive signal processing, image compression, signal and image processing applications as well as transmission of several signals through the same channel. The main idea of using multirate filter banks is the ability of the system to separate in the frequency domain the signal under consideration into two or more signals or to compose two or more different signals into a single signal.

A Review of Physical and Perceptual Feature Extraction Techniques for Speech, Music and Environmental Sounds
Endowing machines with sensing capabilities similar to those of humans is a prevalent quest in engineering and computer science. In the pursuit of making computers sense their surroundings, a huge effort has been conducted to allow machines and computers to acquire, process, analyze and understand their environment in a human-like way. Focusing on the sense of hearing, the ability of computers to sense their acoustic environment as humans do goes by the name of machine hearing. To achieve this ambitious aim, the representation of the audio signal is of paramount importance. In this paper, we present an up-to-date review of the most relevant audio feature extraction techniques developed to analyze the most usual audio signals: speech, music and environmental sounds. Besides revisiting classic approaches for completeness, we include the latest advances in the field based on new domains of analysis together with novel bio-inspired proposals. These approaches are described following a taxonomy that organizes them according to their physical or perceptual basis, being subsequently divided depending on the domain of computation (time, frequency, wavelet, image-based, cepstral, or other domains). The description of the approaches is accompanied with recent examples of their application to machine hearing related problems.

Sum of Two Equal-Frequency Sinusoids
The sum of two equal-frequency real sinusoids is itself a single real sinusoid. However, the exact equations for all the various forms of that single equivalent sinusoid are difficult to find in the signal processing literature. Here we provide those equations.

Design of a Scalable Polyphony-MIDI Synthesizer for a Low Cost DSP
In this thesis, the design of a music synthesizer implementing the Scalable Polyphony-MIDI soundset on a low cost DSP system is presented. First, the SP-MIDI standard and the target DSP platform are presented followed by review of commonly used synthesis techniques and their applicability to systems with limited computational and memory resources. Next, various oscillator and filter algorithms used in digital subtractive synthesis are reviewed in detail. Special attention is given to the aliasing problem caused by discontinuities in classical waveforms, such as sawtooth and pulse waves and existing methods for bandlimited waveform synthesis are presented. This is followed by review of established structures for computationally efficient time-varying filters. A novel digital structure is presented that decouples the cutoff and resonance controls. The new structure is based on the analog Korg MS-20 lowpass filter and is computationally very efficient and well suited for implementation on low bitdepth architectures. Finally, implementation issues are discussed with emphasis on the Differentiated Parabole Wave oscillator and MS-20 filter structures and the effects of limited computational capability and low bitdepth. This is followed by designs for several example instruments.

Optimization of Audio Processing algorithms (Reverb) on ARMv6 family of processors
Audio processing algorithms are increasingly used in cell phones and today’s customers are placing more demands on cell phones. Feature phones, once the advent of mobile phone technology, nowadays do more than just providing the user with MP3 play back or advanced audio effects. These features have become an integral part of medium as well as low-end phones. On the other hand, there is also an endeavor to include as improved quality as possible into products to compete in market and satisfy users’ needs. Tackling the above requirements has been partly satisfied by the advance in hardware design and manufacturing technology. However, as new hardware emerges into market the need for competence to write efficient software and exploit the new features thoroughly and effectively arises. Even though compilers are also keeping up with the new tide space for hand optimized code still exist. Wrapped in the above goal, an effort was made in this thesis to partly cover the competence requirement at Multimedia Section (part of Ericsson Mobile Platforms) to develope optimized code for new processors. Forging persistently ahead with new products, EMP has always incorporated the latest technology into its products among which ARMv6 family of processors has the main central processing role in a number of upcoming products. To fully exploit latest features provided by ARMv6, it was required to probe its new instruction set among which new media processing instructions are of outmost importance. In order to execute DSP-intensive algorithms (e.g. Audio Processing algorithms) efficiently, the implementation should be done in low-level code applying available instruction set. Meanwhile, ARMv6 comes with a number of new features in comparison with its predecessors. SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) and VFP (Vector Floating Point) are the most prominent media processing improvements in ARMv6. Aligned with thesis goals and guidelines, Reverb algorithm which is among one of the most complicated audio features on a hand-held devices was probed. Consequently, its kernel parts were identified and implementation was done both in fixed-point and floating-point using the available resources on hardware. Besides execution time and amount of code memory for each part were measured and provided in tables and charts for comparison purposes. Conclusions were finally drawn based on developed code’s efficiency over ARM compiler’s as well as existing code already developed and tailored to ARMv5 processors. The main criteria for optimization was the execution time. Moreover, quantization effect due to limited precision fixed-point arithmetic was formulated and its effect on quality was elaborated. The outcomes, clearly indicate that hand optimization of kernel parts are superior to Compiler optimized alternative both from the point of code memory as well as execution time. The results also confirmed the presumption that hand optimized code using new instruction set can improve efficiency by an average 25%-50% depending on the algorithm structure and its interaction with other parts of audio effect. Despite its many draw backs, fixed-point implementation remains yet to be the dominant implementation for majority of DSP algorithms on low-power devices.

Peak-to-Average Power Ratio and CCDF
Peak to Average Power Ratio (PAPR) is often used to characterize digitally modulated signals. One example application is setting the level of the signal in a digital modulator. Knowing PAPR allows setting the average power to a level that is just low enough to minimize clipping.

Negative Group Delay
Dispersive linear systems with negative group delay have caused much confusion in the past. Some claim that they violate causality, others that they are the cause of superluminal tunneling. Can we really receive messages before they are sent? This article aims at pouring oil in the fire and causing yet more confusion :-).




















