
Decimator Image Response
This article presents a way to compute and plot the image response of a decimator. I'm defining the image response as the unwanted spectrum of the impulse response after downsampling, relative to the desired passband response.

Filter a Rectangular Pulse with no Ringing
To filter a rectangular pulse without any ringing, there is only one requirement on the filter coefficients: they must all be positive. However, if we want the leading and trailing edge of the pulse to be symmetrical, then the coefficients must be symmetrical. What we are describing is basically a window function.

Digital Envelope Detection: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly
Recently I've been thinking about the process of envelope detection. Tutorial information on this topic is readily available but that information is spread out over a number of DSP textbooks and many Internet web sites. The purpose of this blog is to summarize various digital envelope detection methods in one place. Here I focus of envelope detection as it is applied to an amplitude-fluctuating sinusoidal signal where the positive-amplitude fluctuations (the sinusoid's envelope) contain some sort of information. Let's begin by looking at the simplest envelope detection method.

Python For Audio Signal Processing
This paper discusses the use of Python for developing audio signal processing applications. Overviews of Python language, NumPy, SciPy and Matplotlib are given, which together form a powerful platform for scientific computing. We then show how SciPy was used to create two audio programming libraries, and describe ways that Python can be integrated with the SndObj library and Pure Data, two existing environments for music composition and signal processing.

Lecture Notes on Elliptic Filter Design
Elliptic filters, also known as Cauer or Zolotarev filters, achieve the smallest filter order for the same specifications, or, the narrowest transition width for the same filter order, as compared to other filter types. On the negative side, they have the most nonlinear phase response over their passband. In these notes, we are primarily concerned with elliptic filters. But we will also discuss briefly the design of Butterworth, Chebyshev-1, and Chebyshev-2 filters and present a unified method of designing all cases. We also discuss the design of digital IIR filters using the bilinear transformation method.

Optimizing the Half-band Filters in Multistage Decimation and Interpolation
This article discusses a not so well-known rule regarding the filtering in multistage decimation and interpolation by an integer power of two.
The DFT Magnitude of a Real-valued Cosine Sequence
This article may seem a bit trivial to some readers here but, then again, it might be of some value to DSP beginners. It presents a mathematical proof of what is the magnitude of an N-point discrete Fourier transform (DFT) when the DFT's input is a real-valued sinusoidal sequence.

Sum of Two Equal-Frequency Sinusoids
The sum of two equal-frequency real sinusoids is itself a single real sinusoid. However, the exact equations for all the various forms of that single equivalent sinusoid are difficult to find in the signal processing literature. Here we provide those equations.

Using the DFT as a Filter: Correcting a Misconception
I have read, in some of the literature of DSP, that when the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is used as a filter the process of performing a DFT causes an input signal's spectrum to be frequency translated down to zero Hz (DC). I can understand why someone might say that, but I challenge that statement as being incorrect. Here are my thoughts.

Negative Group Delay
Dispersive linear systems with negative group delay have caused much confusion in the past. Some claim that they violate causality, others that they are the cause of superluminal tunneling. Can we really receive messages before they are sent? This article aims at pouring oil in the fire and causing yet more confusion :-).
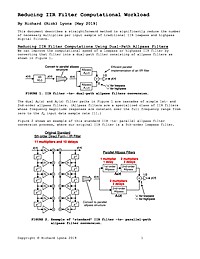
Reducing IIR Filter Computational Workload
This document describes a straightforward method to significantly reduce the number of necessary multiplies per input sample of traditional IIR lowpass and highpass digital filters.

Method to Calculate the Inverse of a Complex Matrix using Real Matrix Inversion
This paper describes a simple method to calculate the invers of a complex matrix. The key element of the method is to use a matrix inversion, which is available and optimised for real numbers. Some actual libraries used for digital signal processing only provide highly optimised methods to calculate the inverse of a real matrix, whereas no solution for complex matrices are available, like in [1]. The presented algorithm is very easy to implement, while still much more efficient than for example the method presented in [2]. [1] Visual DSP++ 4.0 C/C++ Compiler and Library Manual for TigerSHARC Processors; Analog Devices; 2005. [2] W. Press, S.A. Teukolsky, W.T. Vetterling, B.R. Flannery; Numerical Recipes in C++, The art of scientific computing, Second Edition; p52 : “Complex Systems of Equations”;Cambridge University Press 2002.

A Simplified Matlab Function for Power Spectral Density
In an earlier post, I showed how to compute power spectral density (PSD) of a discrete-time signal using the Matlab function pwelch. Pwelch is a useful function because it gives the correct output, and it has the option to average multiple Discrete Fourier Transforms (DFTs). However, a typical function call has five arguments, and it can be hard to remember how to set them all and how they default.
In this post, I create a simplified PSD function by putting a wrapper on pwelch that sets some parameters and converts the output units from W/Hz to dBW/bin. The function is named psd_simple.m, and its code is listed in the appendix.

Digital Filtering in the Frequency Domain
Time domain digital filtering, whether implemented using FIR or IIR techniques, has been very well documented in literature and been thoroughly used in many base band processor designs. However, with the advent of software defined radios as well as CPU support in more recent baseband processors, it has become possible and often desirable to filter signals in software rather than digital hardware. Whereas, time domain digital filtering can certainly be implemented in software as well, it becomes highly inefficient as the number of filter taps grows. Frequency domain filtering, using FFT and IFFT operations, is significantly more efficient and surprisingly easy to understand. This document introduces the reader to frequency domain filtering both in theory and in practice via a MatLab script.
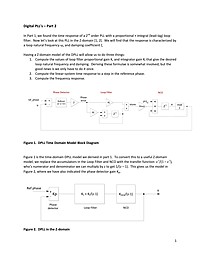
Digital PLL's - Part 2
In Part 1, we found the time response of a 2nd order PLL with a proportional + integral (lead-lag) loop filter. Now let's look at this PLL in the Z-domain.

Computing Translated Frequencies in Digitizing and Downsampling Analog Bandpass Signals
In digital signal processing (DSP) we're all familiar with the processes of bandpass sampling an analog bandpass signal and downsampling a digital bandpass signal. The overall spectral behavior of those operations are well-documented. However, mathematical expressions for computing the translated frequency of individual spectral components, after bandpass sampling or downsampling, are not available in the standard DSP textbooks. This document explains how to compute the frequencies of translated spectral components and provide the desired equations in the hope that they are of use to you.

Fractional Delay FIR Filters
Consider the following Finite Impulse Response (FIR) coefficients:
b = [b0 b1 b2 b1 b0]
These coefficients form a 5-tap symmetrical FIR filter having constant group delay [1,2] over 0 to fs/2 of:
D = (ntaps - 1)/2 = 2 samples
For a symmetrical filter with an odd number of taps, the group delay is always an integer number of samples, while for one with an even number of taps, the group delay is always an integer + 0.5 samples. Can we design a filter with arbitrary delay, say 9.3 samples? The answer is yes -- It is possible to design a non-symmetrical FIR filter with arbitrary group delay which is approximately constant over a wide band, with approximately flat magnitude response [3,4]. Let the desired group delay be:
D = (ntaps - 1)/2 + u
= D0 + u samples, (1)
where we call u the fractional delay and -0.5 <= u <= 0.5. D0 is the fixed portion of the total delay; it is determined by ntaps. The appendix lists a simple Matlab function frac_delay_fir.m to compute FIR coefficients for a given value of u and ntaps. The function provides coefficients with approximately flat delay and frequency responses over a frequency range approaching 0 to fs/2.
In this post, we'll present a couple of examples using the function, then discuss the theory behind it. Finally, we'll look at an example of a fractional delay lowpass FIR filter with arbitrary cut-off frequency.

Optimizing the Half-band Filters in Multistage Decimation and Interpolation
This article discusses a not so well-known rule regarding the filtering in multistage decimation and interpolation by an integer power of two.
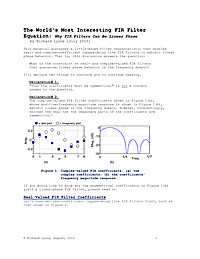
The World's Most Interesting FIR Filter Equation: Why FIR Filters Can Be Linear Phase
This article discusses a little-known filter characteristic that enables real- and complex-coefficient tapped-delay line FIR filters to exhibit linear phase behavior. That is, this article answers the question: What is the constraint on real- and complex-valued FIR filters that guarantee linear phase behavior in the frequency domain?

Lecture Notes on Elliptic Filter Design
Elliptic filters, also known as Cauer or Zolotarev filters, achieve the smallest filter order for the same specifications, or, the narrowest transition width for the same filter order, as compared to other filter types. On the negative side, they have the most nonlinear phase response over their passband. In these notes, we are primarily concerned with elliptic filters. But we will also discuss briefly the design of Butterworth, Chebyshev-1, and Chebyshev-2 filters and present a unified method of designing all cases. We also discuss the design of digital IIR filters using the bilinear transformation method.


















