
Implementing Simultaneous Digital Differentiation, Hilbert Transformation, and Half-Band Filtering
Recently I've been thinking about digital differentiator and Hilbert transformer implementations and I've developed a processing scheme that may be of interest to the readers here on dsprelated.com.
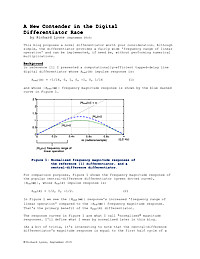
A New Contender in the Digital Differentiator Race
This blog proposes a novel differentiator worth your consideration. Although simple, the differentiator provides a fairly wide 'frequency range of linear operation' and can be implemented, if need be, without performing numerical multiplications.
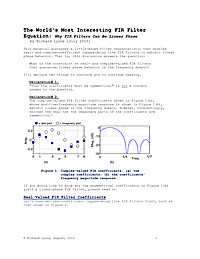
The World's Most Interesting FIR Filter Equation: Why FIR Filters Can Be Linear Phase
This article discusses a little-known filter characteristic that enables real- and complex-coefficient tapped-delay line FIR filters to exhibit linear phase behavior. That is, this article answers the question: What is the constraint on real- and complex-valued FIR filters that guarantee linear phase behavior in the frequency domain?
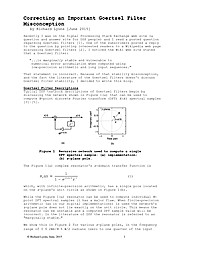
Correcting an Important Goertzel Filter Misconception
Correcting an Important Goertzel Filter Misconception

Complex Down-Conversion Amplitude Loss
This article illustrates the signal amplitude loss inherent in a traditional complex down-conversion system. (In the literature of signal processing, complex down-conversion is also called "quadrature demodulation.")
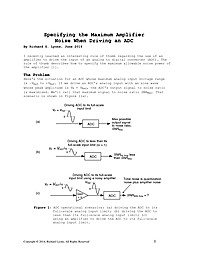
Specifying the Maximum Amplifier Noise When Driving an ADC
I recently learned an interesting rule of thumb regarding the use of an amplifier to drive the input of an analog to digital converter (ADC). The rule of thumb describes how to specify the maximum allowable noise power of the amplifier.

Towards Efficient and Robust Automatic Speech Recognition: Decoding Techniques and Discriminative Training
Automatic speech recognition has been widely studied and is already being applied in everyday use. Nevertheless, the recognition performance is still a bottleneck in many practical applications of large vocabulary continuous speech recognition. Either the recognition speed is not sufficient, or the errors in the recognition result limit the applications. This thesis studies two aspects of speech recognition, decoding and training of acoustic models, to improve speech recognition performance in different conditions.

Introduction to Signal Processing
This book provides an applications-oriented introduction to digital signal processing written primarily for electrical engineering undergraduates. Practicing engineers and graduate students may also find it useful as a first text on the subject.
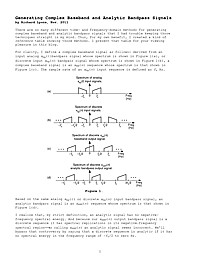
Generating Complex Baseband and Analytic Bandpass Signals
There are so many different time- and frequency-domain methods for generating complex baseband and analytic bandpass signals that I had trouble keeping those techniques straight in my mind. Thus, for my own benefit, I created a kind of reference table showing those methods. I present that table for your viewing pleasure in this document.

Music Signal Processing
Chapter 12 of the book "Multimedia Signal Processing: Theory and Applications in Speech, Music and Communications" - Musical Instruments - A Review of Basic Physics of Sound - Music Signal Features and Models - Ear: Hearing of Sounds - Psychoacoustics of Hearing - Music Compression - High Quality Music Coding: MPEG - Stereo Music - Music Recognition

Acoustic Echo Cancellation using Digital Signal Processing
Acoustic echo cancellation is a common occurrence in todays telecommunication systems. It occurs when an audio source and sink operate in full duplex mode, an example of this is a hands-free loudspeaker telephone. In this situation the received signal is output through the telephone loudspeaker (audio source), this audio signal is then reverberated through the physical environment and picked up by the systems microphone (audio sink). The effect is the return to the distant user of time delayed and attenuated images of their original speech signal. The signal interference caused by acoustic echo is distracting to both users and causes a reduction in the quality of the communication. This thesis focuses on the use of adaptive filtering techniques to reduce this unwanted echo, thus increasing communication quality. Adaptive filters are a class of filters that iteratively alter their parameters in order to minimise a function of the difference between a desired target output and their output. In the case of acoustic echo in telecommunications, the optimal output is an echoed signal that accurately emulates the unwanted echo signal. This is then used to negate the echo in the return signal. The better the adaptive filter emulates this echo, the more successful the cancellation will be. This thesis examines various techniques and algorithms of adaptive filtering, employing discrete signal processing in MATLAB. Also a real-time implementation of an adaptive echo cancellation system has been developed using the Texas Instruments TMS320C6711 DSP development kit.

Specifying the Maximum Amplifier Noise When Driving an ADC
I recently learned an interesting rule of thumb regarding the use of an amplifier to drive the input of an analog to digital converter (ADC). The rule of thumb describes how to specify the maximum allowable noise power of the amplifier.

How Discrete Signal Interpolation Improves D/A Conversion
Earlier this year, for the Linear Audio magazine, published in the Netherlands whose subscribers are technically-skilled hi-fi audio enthusiasts, I wrote an article on the fundamentals of interpolation as it's used to improve the performance of analog-to-digital conversion. Perhaps that article will be of some value to the subscribers of dsprelated.com. Here's what I wrote: We encounter the process of digital-to-analog conversion every day—in telephone calls (land lines and cell phones), telephone answering machines, CD & DVD players, iPhones, digital television, MP3 players, digital radio, and even talking greeting cards. This material is a brief tutorial on how sample rate conversion improves the quality of digital-to-analog conversion.

Fixed-Point Arithmetic: An Introduction
This document presents definitions of signed and unsigned fixed-point binary number representations and develops basic rules and guidelines for the manipulation of these number representations using the common arithmetic and logical operations found in fixed-point DSPs and hardware components.

Hilbert Transform and Applications
Section 1: reviews the mathematical definition of Hilbert transform and various ways to calculate it.
Sections 2 and 3: review applications of Hilbert transform in two major areas: Signal processing and system identification.
Section 4: concludes with remarks on the historical development of Hilbert transform

Voice Activity Detection. Fundamentals and Speech Recognition System Robustness
An important drawback affecting most of the speech processing systems is the environmental noise and its harmful effect on the system performance. Examples of such systems are the new wireless communications voice services or digital hearing aid devices. In speech recognition, there are still technical barriers inhibiting such systems from meeting the demands of modern applications. Numerous noise reduction techniques have been developed to palliate the effect of the noise on the system performance and often require an estimate of the noise statistics obtained by means of a precise voice activity detector (VAD). Speech/non-speech detection is an unsolved problem in speech processing and affects numerous applications including robust speech recognition, discontinuous transmission, real-time speech transmission on the Internet or combined noise reduction and echo cancellation schemes in the context of telephony. The speech/non-speech classification task is not as trivial as it appears, and most of the VAD algorithms fail when the level of background noise increases. During the last decade, numerous researchers have developed different strategies for detecting speech on a noisy signal and have evaluated the influence of the VAD effectiveness on the performance of speech processing systems. Most of the approaches have focussed on the development of robust algorithms with special attention being paid to the derivation and study of noise robust features and decision rules. The different VAD methods include those based on energy thresholds, pitch detection, spectrum analysis, zero-crossing rate, periodicity measure, higher order statistics in the LPC residual domain or combinations of different features. This chapter shows a comprehensive approximation to the main challenges in voice activity detection, the different solutions that have been reported in a complete review of the state of the art and the evaluation frameworks that are normally used. The application of VADs for speech coding, speech enhancement and robust speech recognition systems is shown and discussed. Three different VAD methods are described and compared to standardized and recently reported strategies by assessing the speech/non-speech discrimination accuracy and the robustness of speech recognition systems.






















