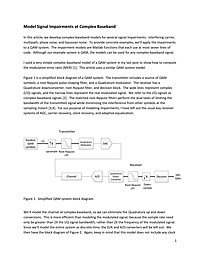
Model Signal Impairments at Complex Baseband
In this article, we develop complex-baseband models for several signal impairments: interfering carrier, multipath, phase noise, and Gaussian noise. To provide concrete examples, we'll apply the impairments to a QAM system. The impairment models are Matlab functions that each use at most seven lines of code. Although our example system is QAM, the models can be used for any complex-baseband signal.
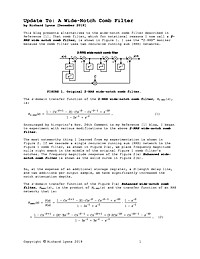
Update To: A Wide-Notch Comb Filter
This article presents alternatives to the wide-notch comb filter described in Reference [1].
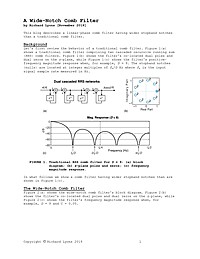
A Wide-Notch Comb Filter
This article describes a linear-phase comb filter having wider stopband notches than a traditional comb filter.

The Risk In Using Frequency Domain Curves To Evaluate Digital Integrator Performance
This article shows the danger in evaluating the performance of a digital integration network based solely on its frequency response curve. If you plan on implementing a digital integrator in your signal processing work I recommend you continue reading this article.
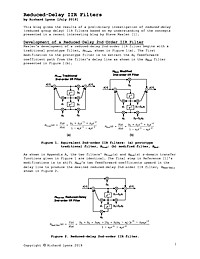
Reduced-Delay IIR Filters
This document describes a straightforward method to significantly reduce the number of necessary multiplies per input sample of traditional IIR lowpass and highpass digital filters.
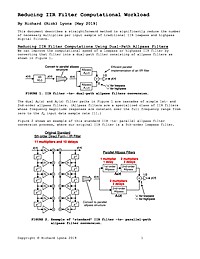
Reducing IIR Filter Computational Workload
This document describes a straightforward method to significantly reduce the number of necessary multiplies per input sample of traditional IIR lowpass and highpass digital filters.
An Experimental Multichannel Pulse Code Modulation System of Toll Quality + Electron Beam Deflection Tube For Pulse Code Modulation
See this blog post for context. Pulse Code Modulation offers attractive possibilities for multiplex telephony via such media as the microwave radio relay. The various problems involved in its use have been explored in terms of a 96-channel system designed to meet the transmission requirements commonly imposed upon commercial toll circuits. Twenty-four of the 96 channels have been fully equipped in an experimental model of the system. Coding and decoding devices are described, along with other circuit details. The coder is based upon a new electron beam tube, and is characterized by speed and simplicity as well as accuracy of coding. These qualities are matched in the decoder, which employs pulse excitation of a simple reactive network.

Use Matlab Function pwelch to Find Power Spectral Density - or Do It Yourself
In this article, I'll present some examples to show how to use pwelch. You can also "do it yourself", i.e. compute spectra using the Matlab fft or other fft function. As examples, the appendix provides two demonstration mfiles; one computes the spectrum without DFT averaging, and the other computes the spectrum with DFT averaging.

Design IIR Filters Using Cascaded Biquads
This article shows how to implement a Butterworth IIR lowpass filter as a cascade of second-order IIR filters, or biquads. We'll derive how to calculate the coefficients of the biquads and do some examples using a Matlab function biquad_synth provided in the Appendix. Although we'll be designing Butterworth filters, the approach applies to any all-pole lowpass filter (Chebyshev, Bessel, etc). As we'll see, the cascaded-biquad design is less sensitive to coefficient quantization than a single high-order IIR, particularly for lower cut-off frequencies.

Python For Audio Signal Processing
This paper discusses the use of Python for developing audio signal processing applications. Overviews of Python language, NumPy, SciPy and Matplotlib are given, which together form a powerful platform for scientific computing. We then show how SciPy was used to create two audio programming libraries, and describe ways that Python can be integrated with the SndObj library and Pure Data, two existing environments for music composition and signal processing.
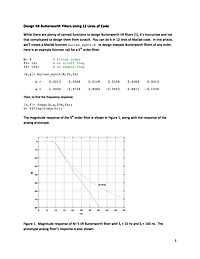
Design IIR Butterworth Filters Using 12 Lines of Code
While there are plenty of canned functions to design Butterworth IIR filters [1], it's instructive and not that complicated to design them from scratch. You can do it in 12 lines of Matlab code.

Introduction to Real-Time Digital Signal Processing
Chapter 1 of the book: Real-Time Digital Signal Processing: Fundamentals, Implementations and Applications, 3rd Edition

Design IIR Filters Using Cascaded Biquads
This article shows how to implement a Butterworth IIR lowpass filter as a cascade of second-order IIR filters, or biquads. We'll derive how to calculate the coefficients of the biquads and do some examples using a Matlab function biquad_synth provided in the Appendix. Although we'll be designing Butterworth filters, the approach applies to any all-pole lowpass filter (Chebyshev, Bessel, etc). As we'll see, the cascaded-biquad design is less sensitive to coefficient quantization than a single high-order IIR, particularly for lower cut-off frequencies.

Digital PLL's -- Part 1
We will use Matlab to model the DPLL in the time and frequency domains (Simulink is also a good tool for modeling a DPLL in the time domain). Part 1 discusses the time domain model; the frequency domain model will be covered in Part 2. The frequency domain model will allow us to calculate the loop filter parameters to give the desired bandwidth and damping, but it is a linear model and cannot predict acquisition behavior. The time domain model can be made almost identical to the gate-level system, and as such, is able to model acquisition.
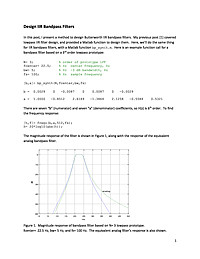
Design IIR Bandpass Filters
In this post, I present a method to design Butterworth IIR bandpass filters. My previous post [1] covered lowpass IIR filter design, and provided a Matlab function to design them. Here, we'll do the same thing for IIR bandpass filters, with a Matlab function bp_synth.m

Digital Signal Processor Fundamentals and System Design
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) have been used in accelerator systems for more than fifteen years and have largely contributed to the evolution towards digital technology of many accelerator systems, such as machine protection, diagnostics and control of beams, power supply and motors. This paper aims at familiarising the reader with DSP fundamentals, namely DSP characteristics and processing development. Several DSP examples are given, in particular on Texas Instruments DSPs, as they are used in the DSP laboratory companion of the lectures this paper is based upon. The typical system design flow is described; common difficulties, problems and choices faced by DSP developers are outlined; and hints are given on the best solution.

Use Matlab Function pwelch to Find Power Spectral Density - or Do It Yourself
In this article, I'll present some examples to show how to use pwelch. You can also "do it yourself", i.e. compute spectra using the Matlab fft or other fft function. As examples, the appendix provides two demonstration mfiles; one computes the spectrum without DFT averaging, and the other computes the spectrum with DFT averaging.

A Pragmatic Introduction to Signal Processing
An illustrated essay with software available for free download.




















