
Simplest Calculation of Half-band Filter Coefficients
Half-band filters are lowpass FIR filters with cut-off frequency of one-quarter of sampling frequency fs and odd symmetry about fs/4 [1]*. And it so happens that almost half of the coefficients are zero. The passband and stopband bandwiths are equal, making these filters useful for decimation-by-2 and interpolation-by-2. Since the zero coefficients make them computationally efficient, these filters are ubiquitous in DSP systems. Here we will compute half-band coefficients using the window method. While the window method typically does not yield the fewest taps for a given performance, it is useful for learning about half-band filters. Efficient equiripple half-band filters can be designed using the Matlab function firhalfband [2].

Errata for the book: 'Understanding Digital Signal Processing'
Errata 3rd Ed. International Version.pdfErrata 3rd Ed. International Version.pdfThis blog post provides, in one place, the errata for each of the many different Editions/Printings of my book Understanding Digital Signal Processing. If you...

Feedback Controllers - Making Hardware with Firmware. Part I. Introduction
Introduction to the topic This is the 1st in a series of articles looking at how we can use DSP and Feedback Control Sciences along with some mixed-signal electronics and number-crunching capability (e.g. FPGA), to create arbitrary...

How to Find a Fast Floating-Point atan2 Approximation
Context Over a short period of time, I came across nearly identical approximations of the two parameter arctangent function, atan2, developed by different companies, in different countries, and even in different decades. Fascinated...

A Beginner's Guide to OFDM
In the recent past, high data rate wireless communications is often considered synonymous to an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system. OFDM is a special case of multi-carrier communication as opposed to a conventional...
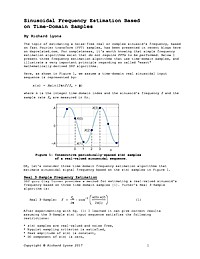
Sinusoidal Frequency Estimation Based on Time-Domain Samples
The topic of estimating a noise-free real or complex sinusoid's frequency, based on fast Fourier transform (FFT) samples, has been presented in recent blogs here on dsprelated.com. For completeness, it's worth knowing that simple frequency estimation algorithms exist that do not require FFTs to be performed . Below I present three frequency estimation algorithms that use time-domain samples, and illustrate a very important principle regarding so called "exact" mathematically-derived DSP algorithms.

Launch of Youtube Channel: My First Videos - Embedded World 2017
I went to Embedded World 2017 in Nuremberg with an ambitious plan; I would make video highlights of several exhibits (booths) to be presented to the *Related sites audience. I would try to make the vendors focus their pitch on the essential...

A Two Bin Exact Frequency Formula for a Pure Complex Tone in a DFT
Introduction This is an article to hopefully give a better understanding to the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) by deriving an exact formula for the frequency of a complex tone in a DFT. It is basically a parallel treatment to the real case...

DFT Bin Value Formulas for Pure Complex Tones
Introduction This is an article to hopefully give a better understanding to the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) by deriving an analytical formula for the DFT of pure complex tones and an alternative variation. It is basically a parallel...

Multi-Decimation Stage Filtering: Design and Optimization
During my research on digital FIR decimation filters I have been developing various Matlab scripts and functions. In which I have decided later on to consolidate it in a form of a toolbox. I have developed this toolbox to assist and...

Spectral Flipping Around Signal Center Frequency
Most of us are familiar with the process of flipping the spectrum (spectral inversion) of a real signal by multiplying that signal's time samples by (-1)n. In that process the center of spectral rotation is fs/4, where fs is the signal's sample...

Return of the Delta-Sigma Modulators, Part 1: Modulation
About a decade ago, I wrote two articles: Modulation Alternatives for the Software Engineer (November 2011) Isolated Sigma-Delta Modulators, Rah Rah Rah! (April 2013) Each of these are about delta-sigma modulation, but they’re...
A New Contender in the Quadrature Oscillator Race
There have been times when I wanted to determine the z-domain transfer function of some discrete network, but my algebra skills failed me. Some time ago I learned Mason's Rule, which helped me solve my problems. If you're willing to learn the...
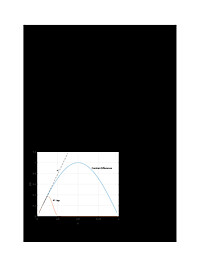
Evaluate Noise Performance of Discrete-Time Differentiators
When it comes to noise, all differentiators are not created equal. Figure 1 shows the magnitude response of two differentiators. They both have a useful bandwidth of a little less than π/8 radians (based on maximum magnitude response...

Errata for the book: 'Understanding Digital Signal Processing'
Errata 3rd Ed. International Version.pdfErrata 3rd Ed. International Version.pdfThis blog post provides, in one place, the errata for each of the many different Editions/Printings of my book Understanding Digital Signal Processing. If you...

Feedback Controllers - Making Hardware with Firmware. Part I. Introduction
Introduction to the topic This is the 1st in a series of articles looking at how we can use DSP and Feedback Control Sciences along with some mixed-signal electronics and number-crunching capability (e.g. FPGA), to create arbitrary...
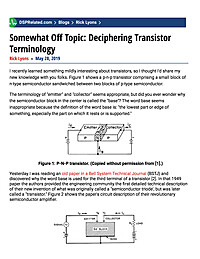
Somewhat Off Topic: Deciphering Transistor Terminology
I recently learned something mildly interesting about transistors, so I thought I'd share my new knowledge with you folks. Figure 1 shows a p-n-p transistor comprising a small block of n-type semiconductor sandwiched between two blocks of p-type...
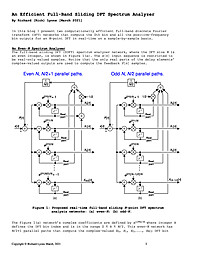
An Efficient Full-Band Sliding DFT Spectrum Analyzer
In this blog I present two computationally efficient full-band discrete Fourier transform (DFT) networks that compute the 0th bin and all the positive-frequency bin outputs for an N-point DFT in real-time on a sample-by-sample basis. An Even-N...
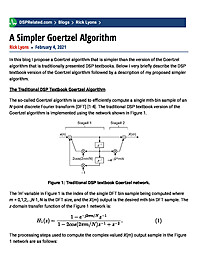
A Simpler Goertzel Algorithm
In this blog I propose a Goertzel algorithm that is simpler than the version of the Goertzel algorithm that is traditionally presented DSP textbooks. Below I very briefly describe the DSP textbook version of the Goertzel algorithm followed by a...

A Free DSP Laboratory
Getting Started In Audio DSPImagine you're starting out studying DSP and your particular interest is audio. Wouldn't it be nice to have access to some audio signals and the tools to analyze and modify them? In the old days, a laboratory like this...


















