Scattering at Impedance Changes
When a traveling wave encounters a change in wave impedance, scattering occurs, i.e., a traveling wave impinging on an impedance discontinuity will partially reflect and partially transmit at the junction in such a way that energy is conserved. This is a classical topic in transmission line theory [295], and it is well covered for acoustic tubes in a variety of references [297,363]. However, for completeness, we derive the basic scattering relations below for plane waves in air, and for longitudinal stress waves in rods.
Plane-Wave Scattering
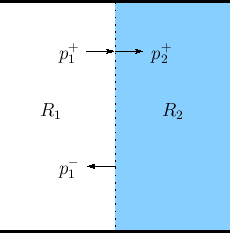
Consider a plane wave with peak pressure amplitude ![]() propagating
from wave impedance
propagating
from wave impedance ![]() into a new wave impedance
into a new wave impedance ![]() , as shown in
Fig.C.15. (Assume
, as shown in
Fig.C.15. (Assume ![]() and
and ![]() are real and positive.)
The physical constraints on the wave are that
are real and positive.)
The physical constraints on the wave are that
- pressure must be continuous everywhere, and
- velocity in must equal velocity out (the junction has no state).

As derived in §C.7.3, we also have the Ohm's law relations:

To obey the physical constraints at the impedance discontinuity, the
incident plane-wave must split into a reflected plane wave
![]() and a transmitted plane-wave
and a transmitted plane-wave ![]() such that
pressure is continuous and signal power is conserved. The physical
pressure on the left of the junction is
such that
pressure is continuous and signal power is conserved. The physical
pressure on the left of the junction is
![]() , and the
physical pressure on the right of the junction is
, and the
physical pressure on the right of the junction is
![]() , since
, since ![]() according to our set-up.
according to our set-up.
Scattering Solution
Define the junction pressure ![]() and junction velocity
and junction velocity ![]() by
by
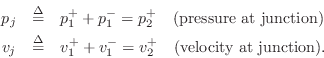
Then we can write
![\begin{eqnarray*}
p^+_1+p^-_1 &=& p^+_2\;=\;p_j\\ [10pt]
\,\,\Rightarrow\,\,R_1v...
...\\ [10pt]
\,\,\Rightarrow\,\,2\,R_1v^{+}_1 - R_1 v_j &=& R_2 v_j
\end{eqnarray*}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3532.png)
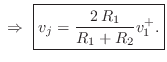
![$\displaystyle v^{-}_1 = v_j - v^{+}_1 = \left[\frac{2\,R_1}{R_1+R_2} - 1\right]v^{+}_1 = \frac{R_1-R_2}{R_1+R_2} v^{+}_1.
$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3536.png)
Using the Ohm's law relations, the pressure waves follow easily:
![\begin{eqnarray*}
p^+_2 &=& R_2v^{+}_2 = R_2 v_j = \frac{2\,R_2}{R_1+R_2}p^+_1\\ [10pt]
p^-_1 &=& -R_1v^{-}_1 = \frac{R_2-R_1}{R_1+R_2} p^+_1
\end{eqnarray*}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3537.png)
Reflection Coefficient
Define the reflection coefficient of the scattering junction as

![\begin{eqnarray*}
p^+_2 &=& (1+\rho)p^+_1\\ [3pt]
p^-_1 &=& \rho\,p^+_1
\end{eqnarray*}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3539.png)
Signal flow graphs for pressure and velocity are given in Fig.C.16.
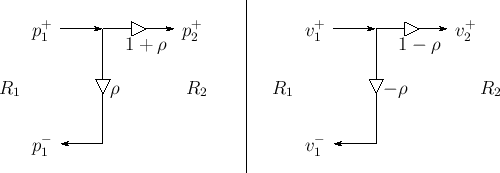 |
It is a simple exercise to verify that signal power is conserved by
checking that
![]() .
(Left-going power is negated to account for its opposite
direction-of-travel.)
.
(Left-going power is negated to account for its opposite
direction-of-travel.)
So far we have only considered a plane wave incident on the left of
the junction. Consider now a plane wave incident from the right. For
that wave, the impedance steps from ![]() to
to ![]() , so the reflection
coefficient it ``sees'' is
, so the reflection
coefficient it ``sees'' is ![]() . By superposition, the signal flow
graph for plane waves incident from either side is given by
Fig.C.17. Note that the transmission coefficient is
one plus the reflection coefficient in either direction. This signal
flow graph is often called the ``Kelly-Lochbaum'' scattering junction
[297].
. By superposition, the signal flow
graph for plane waves incident from either side is given by
Fig.C.17. Note that the transmission coefficient is
one plus the reflection coefficient in either direction. This signal
flow graph is often called the ``Kelly-Lochbaum'' scattering junction
[297].
 |
There are some simple special cases:
-
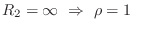 (e.g., rigid wall reflection)
(e.g., rigid wall reflection)
-
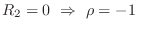 (e.g., open-ended tube)
(e.g., open-ended tube)
-
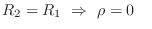 (no reflection)
(no reflection)
Plane-Wave Scattering at an Angle
Figure C.18 shows the more general situation (as compared
to Fig.C.15) of a sinusoidal traveling plane wave
encountering an impedance discontinuity at some arbitrary angle of
incidence, as indicated by the vector wavenumber
![]() . The
mathematical details of general sinusoidal plane waves in air and
vector wavenumber are reviewed in §B.8.1.
. The
mathematical details of general sinusoidal plane waves in air and
vector wavenumber are reviewed in §B.8.1.
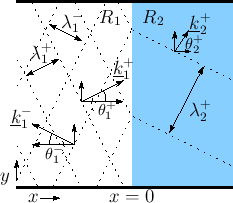 |
At the boundary between impedance ![]() and
and ![]() , we have, by
continuity of pressure,
, we have, by
continuity of pressure,
as we will now derive.
Let the impedance change be in the
![]() plane. Thus, the
impedance is
plane. Thus, the
impedance is ![]() for
for ![]() and
and ![]() for
for ![]() . There are three
plane waves to consider:
. There are three
plane waves to consider:
- The incident plane wave with wave vector

- The reflected plane wave with wave vector
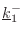
- The transmitted plane wave with wave vector
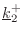
where
Reflection and Refraction
The first equality in Eq.![]() (C.56) implies that the
angle of incidence equals angle of reflection:
(C.56) implies that the
angle of incidence equals angle of reflection:
We now wish to find the wavenumber in medium 2.
Let ![]() denote the phase velocity in wave impedance
denote the phase velocity in wave impedance ![]() :
:
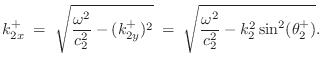
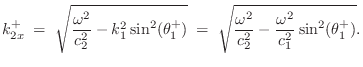
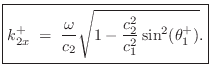
Evanescent Wave due to Total Internal Reflection
Note that if
![]() , the horizontal component
of the wavenumber in medium 2 becomes imaginary. In this case,
the wave in medium 2 is said to be evanescent, and the wave in
medium 1 undergoes total internal reflection (no power travels
from medium 1 to medium 2). The evanescent-wave amplitude decays
exponentially to the right and oscillates ``in place'' (like a
standing wave). ``Tunneling'' is possible given a
medium 3 beyond medium 2 in which wave propagation resumes.
, the horizontal component
of the wavenumber in medium 2 becomes imaginary. In this case,
the wave in medium 2 is said to be evanescent, and the wave in
medium 1 undergoes total internal reflection (no power travels
from medium 1 to medium 2). The evanescent-wave amplitude decays
exponentially to the right and oscillates ``in place'' (like a
standing wave). ``Tunneling'' is possible given a
medium 3 beyond medium 2 in which wave propagation resumes.
To show explicitly the exponential decay and in-place oscillation in
an evanescent wave, express the imaginary wavenumber as
![]() . Then we have
. Then we have
![\begin{eqnarray*}
p(t,\underline{x}) &=&
\cos\left(\omega t - \underline{k}^T\...
...-k_x x}\right\}}}\\ [5pt]
&=& e^{-k_x x} \cos(\omega t - k_y y).
\end{eqnarray*}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3576.png)
Thus, an imaginary wavenumber corresponds to an exponentially decaying evanescent wave. Note that the time dependence (cosine term) applies to all points to the right of the boundary. Since evanescent waves do not really ``propagate,'' it is perhaps better to speak of an ``evanescent acoustic field'' or ``evanescent standing wave'' instead of ``evanescent waves''.
For more on the physics of evanescent waves and tunneling, see [295].
Longitudinal Waves in Rods
In this section, elementary scattering relations will be derived for the case of longitudinal force and velocity waves in an ideal string or rod. In solids, force-density waves are referred to as stress waves [169,261]. Longitudinal stress waves in strings and rods have units of (compressive) force per unit area and are analogous to longitudinal pressure waves in acoustic tubes.
![\includegraphics[width=\twidth]{eps/Fwgfs}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3577.png) |
A single waveguide section between two partial sections is shown in
Fig.C.19. The sections are numbered 0 through ![]() from
left to right, and their wave impedances are
from
left to right, and their wave impedances are ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() ,
respectively. Such a rod might be constructed, for example, using
three different materials having three different densities. In the
,
respectively. Such a rod might be constructed, for example, using
three different materials having three different densities. In the
![]() th section, there are two stress traveling waves:
th section, there are two stress traveling waves: ![]() traveling
to the right at speed
traveling
to the right at speed ![]() , and
, and ![]() traveling to the left at speed
traveling to the left at speed
![]() . To minimize the numerical dynamic range, velocity waves may be
chosen instead when
. To minimize the numerical dynamic range, velocity waves may be
chosen instead when ![]() .
.
As in the case of transverse waves (see the derivation of (C.46)), the traveling longitudinal plane waves in each section satisfy [169,261]
where the wave impedance is now
If the wave impedance ![]() is constant, the shape of a traveling wave
is not altered as it propagates from one end of a rod-section to the
other. In this case we need only consider
is constant, the shape of a traveling wave
is not altered as it propagates from one end of a rod-section to the
other. In this case we need only consider ![]() and
and ![]() at one
end of each section as a function of time. As shown in Fig.C.19,
we define
at one
end of each section as a function of time. As shown in Fig.C.19,
we define
![]() as the force-wave component at the extreme
left of section
as the force-wave component at the extreme
left of section ![]() . Therefore, at the extreme right of section
. Therefore, at the extreme right of section ![]() ,
we have the traveling waves
,
we have the traveling waves
![]() and
and
![]() , where
, where ![]() is
the travel time from one end of a section to the other.
is
the travel time from one end of a section to the other.
For generality, we may allow the wave impedances ![]() to vary with
time. A number of possibilities exist which satisfy (C.57) in the
time-varying case. For the moment, we will assume the traveling waves
at the extreme right of section
to vary with
time. A number of possibilities exist which satisfy (C.57) in the
time-varying case. For the moment, we will assume the traveling waves
at the extreme right of section ![]() are still given by
are still given by
![]() and
and
![]() . This definition, however, implies the velocity varies
inversely with the wave impedance. As a result, signal energy, being the product
of force times velocity, is ``pumped'' into or out of the waveguide
by a changing wave impedance. Use of normalized waves
. This definition, however, implies the velocity varies
inversely with the wave impedance. As a result, signal energy, being the product
of force times velocity, is ``pumped'' into or out of the waveguide
by a changing wave impedance. Use of normalized waves
![]() avoids this.
However, normalization increases the required number of
multiplications, as we will see in §C.8.6 below.
avoids this.
However, normalization increases the required number of
multiplications, as we will see in §C.8.6 below.
As before, the physical force density (stress) and velocity at the
left end of section ![]() are obtained by summing the left- and
right-going traveling wave components:
are obtained by summing the left- and
right-going traveling wave components:
Let
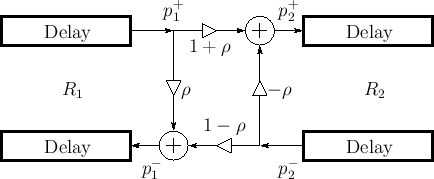
Kelly-Lochbaum Scattering Junctions
Conservation of energy and mass dictate that, at the impedance
discontinuity, force and velocity variables must be continuous
where velocity is defined as positive to the right on both sides of the junction. Force (or stress or pressure) is a scalar while velocity is a vector with both a magnitude and direction (in this case only left or right). Equations (C.57), (C.58), and (C.59) imply the following scattering equations (a derivation is given in the next section for the more general case of
where
is called the
The scattering equations are illustrated in Figs. C.19b and C.20. In linear predictive coding of speech [482], this structure is called the Kelly-Lochbaum scattering junction, and it is one of several types of scattering junction used to implement lattice and ladder digital filter structures (§C.9.4,[297]).
One-Multiply Scattering Junctions
By factoring out ![]() in each equation of (C.60), we can write
in each equation of (C.60), we can write
where
Thus, only one multiplication is actually necessary to compute the transmitted and reflected waves from the incoming waves in the Kelly-Lochbaum junction. This computation is shown in Fig.C.21, and it is known as the one-multiply scattering junction [297].
Another one-multiply form is obtained by organizing (C.60) as
where
As in the previous case, only one multiplication and three additions are required per junction. This one-multiply form generalizes more readily to junctions of more than two waveguides, as we'll see in a later section.
A scattering junction well known in the LPC speech literature but not described here is the so-called two-multiply junction [297] (requiring also two additions). This omission is because the two-multiply junction is not valid as a general, local, physical modeling building block. Its derivation is tied to the reflectively terminated, cascade waveguide chain. In cases where it applies, however, it can be the implementation of choice; for example, in DSP chips having a fast multiply-add instruction, it may be possible to implement the inner loop of the two-multiply, two-add scattering junction using only two instructions.
Normalized Scattering Junctions
Using (C.53) to convert to normalized waves
![]() , the
Kelly-Lochbaum junction (C.60) becomes
, the
Kelly-Lochbaum junction (C.60) becomes
as diagrammed in Fig.C.22. This is called the normalized scattering junction [297], although a more precise term would be the ``normalized-wave scattering junction.''
It is interesting to define
![]() , always
possible for passive junctions since
, always
possible for passive junctions since
![]() , and note that
the normalized scattering junction is equivalent to a 2D rotation:
, and note that
the normalized scattering junction is equivalent to a 2D rotation:
where, for conciseness of notation, the time-invariant case is written.
While it appears that scattering of normalized waves at a two-port junction requires four multiplies and two additions, it is possible to convert this to three multiplies and three additions using a two-multiply ``transformer'' to power-normalize an ordinary one-multiply junction [432].
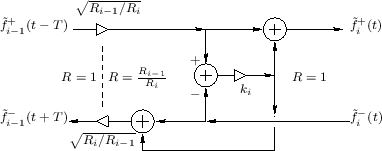
The transformer is a lossless two-port defined by [136]
The transformer can be thought of as a device which steps the wave impedance to a new value without scattering; instead, the traveling signal power is redistributed among the force and velocity wave variables to satisfy the fundamental relations
as can be quickly derived by requiring
Figure C.23 illustrates a three-multiply
normalized-wave scattering junction [432]. The impedance of
all waveguides (bidirectional delay lines) may be taken to be ![]() .
Scattering junctions may then be implemented as a denormalizing
transformer
.
Scattering junctions may then be implemented as a denormalizing
transformer
![]() , a one-multiply scattering junction
, a one-multiply scattering junction
![]() , and a renormalizing transformer
, and a renormalizing transformer
![]() . Either
transformer may be commuted with the junction and combined with the
other transformer to give a three-multiply normalized-wave scattering
junction. (The transformers are combined on the left in
Fig.C.23).
. Either
transformer may be commuted with the junction and combined with the
other transformer to give a three-multiply normalized-wave scattering
junction. (The transformers are combined on the left in
Fig.C.23).
In slightly more detail, a transformer
![]() steps the wave
impedance (left-to-right) from
steps the wave
impedance (left-to-right) from ![]() to
to ![]() . Equivalently, the
normalized force-wave
. Equivalently, the
normalized force-wave
![]() is converted unnormalized form
is converted unnormalized form
![]() . Next there is a physical scattering from impedance
. Next there is a physical scattering from impedance
![]() to
to ![]() (reflection coefficient
(reflection coefficient
![]() ). The outgoing wave to the right is
then normalized by transformer
). The outgoing wave to the right is
then normalized by transformer
![]() to return the wave
impedance back to
to return the wave
impedance back to ![]() for wave propagation within a normalized-wave
delay line to the right. Finally, the right transformer is commuted
left and combined with the left transformer to reduce total
computational complexity to one multiply and three adds.
for wave propagation within a normalized-wave
delay line to the right. Finally, the right transformer is commuted
left and combined with the left transformer to reduce total
computational complexity to one multiply and three adds.
It is important to notice that transformer-normalized junctions may
have a large dynamic range in practice. For example, if
![]() , then Eq.
, then Eq.![]() (C.69) shows that the
transformer coefficients may become as large as
(C.69) shows that the
transformer coefficients may become as large as
![]() . If
. If ![]() is the ``machine epsilon,'' i.e.,
is the ``machine epsilon,'' i.e.,
![]() for typical
for typical ![]() -bit two's complement arithmetic normalized
to lie in
-bit two's complement arithmetic normalized
to lie in ![]() , then the dynamic range of the transformer
coefficients is bounded by
, then the dynamic range of the transformer
coefficients is bounded by
![]() . Thus, while
transformer-normalized junctions trade a multiply for an add, they
require up to
. Thus, while
transformer-normalized junctions trade a multiply for an add, they
require up to ![]() % more bits of dynamic range within the junction
adders. On the other hand, it is very nice to have normalized waves
(unit wave impedance) throughout the digital waveguide network,
thereby limiting the required dynamic range to root physical power in
all propagation paths.
% more bits of dynamic range within the junction
adders. On the other hand, it is very nice to have normalized waves
(unit wave impedance) throughout the digital waveguide network,
thereby limiting the required dynamic range to root physical power in
all propagation paths.
Junction Passivity
In fixed-point implementations, the round-off error and other nonlinear operations should be confined when possible to physically meaningful wave variables. When this is done, it is easy to ensure that signal power is not increased by the nonlinear operations. In other words, nonlinear operations such as rounding can be made passive. Since signal power is proportional to the square of the wave variables, all we need to do is make sure amplitude is never increased by the nonlinearity. In the case of rounding, magnitude truncation, sometimes called ``rounding toward zero,'' is one way to achieve passive rounding. However, magnitude truncation can attenuate the signal excessively in low-precision implementations and in scattering-intensive applications such as the digital waveguide mesh [518]. Another option is error power feedback in which case the cumulative round-off error power averages to zero over time.
A valuable byproduct of passive arithmetic is the suppression of limit cycles and overflow oscillations [432]. Formally, the signal power of a conceptually infinite-precision implementation can be taken as a Lyapunov function bounding the squared amplitude of the finite-precision implementation.
The Kelly-Lochbaum and one-multiply scattering junctions are structurally lossless [500,460] (see also
§C.17) because they have only one parameter ![]() (or
(or
![]() ), and all quantizations of the parameter within the allowed
interval
), and all quantizations of the parameter within the allowed
interval ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) correspond to lossless
scattering.C.6
) correspond to lossless
scattering.C.6
In the Kelly-Lochbaum and one-multiply scattering junctions, because they are structurally lossless, we need only double the number of bits at the output of each multiplier, and add one bit of extended dynamic range at the output of each two-input adder. The final outgoing waves are thereby exactly computed before they are finally rounded to the working precision and/or clipped to the maximum representable magnitude.
For the Kelly-Lochbaum scattering junction, given ![]() -bit signal samples
and
-bit signal samples
and ![]() -bit reflection coefficients, the reflection and transmission
multipliers produce
-bit reflection coefficients, the reflection and transmission
multipliers produce ![]() and
and ![]() bits, respectively, and each of the
two additions adds one more bit. Thus, the intermediate word length
required is
bits, respectively, and each of the
two additions adds one more bit. Thus, the intermediate word length
required is ![]() bits, and this must be rounded without
amplification down to
bits, and this must be rounded without
amplification down to ![]() bits for the final outgoing samples. A similar
analysis gives also that the one-multiply scattering junction needs
bits for the final outgoing samples. A similar
analysis gives also that the one-multiply scattering junction needs ![]() bits for the extended precision intermediate results before final rounding
and/or clipping.
bits for the extended precision intermediate results before final rounding
and/or clipping.
To formally show that magnitude truncation is sufficient to suppress
overflow oscillations and limit cycles in waveguide networks built using
structurally lossless scattering junctions, we can look at the signal power
entering and leaving the junction. A junction is passive if the power
flowing away from it does not exceed the power flowing into it. The total
power flowing away from the ![]() th junction is bounded by the incoming power
if
th junction is bounded by the incoming power
if
Let
Thus, if the junction computations do not increase either of the output force amplitudes, no signal power is created. An analogous conclusion is reached for velocity scattering junctions.
Unlike the structurally lossless cases, the (four-multiply) normalized
scattering junction has two parameters,
![]() and
and
![]() , and these can ``get out of synch'' in the
presence of quantization. Specifically, let
, and these can ``get out of synch'' in the
presence of quantization. Specifically, let
![]() denote the quantized value of
denote the quantized value of ![]() , and let
, and let
![]() denote the quantized value of
denote the quantized value of ![]() . Then it is no longer the
case in general that
. Then it is no longer the
case in general that
![]() . As a result, the
normalized scattering junction is not structurally lossless in the presence
of coefficient quantization. A few lines of algebra shows that a passive
rounding rule for the normalized junction must depend on the sign of the
wave variable being computed, the sign of the coefficient quantization
error, and the sign of at least one of the two incoming traveling waves.
We can assume one of the coefficients is exact for passivity purposes, so
assume
. As a result, the
normalized scattering junction is not structurally lossless in the presence
of coefficient quantization. A few lines of algebra shows that a passive
rounding rule for the normalized junction must depend on the sign of the
wave variable being computed, the sign of the coefficient quantization
error, and the sign of at least one of the two incoming traveling waves.
We can assume one of the coefficients is exact for passivity purposes, so
assume
![]() and define
and define
![]() , where
, where
![]() denotes largest quantized value less than or equal to
denotes largest quantized value less than or equal to ![]() .
In this case we have
.
In this case we have
![]() . Therefore,
. Therefore,
The three-multiply normalized scattering junction is easier to ``passify.''
While the transformer is not structurally lossless, its simplicity allows
it to be made passive simply by using non-amplifying rounding on both of
its coefficients as well as on its output wave variables. (The transformer
is passive when the product of its coefficients has magnitude less than or
equal to ![]() .) Since there are no additions following the transformer
multiplies, double-precision adders are not needed. However, precision and
a half is needed in the junction adders to accommodate the worst-case
increased dynamic range. Since the one-multiply junction is structurally
lossless, the overall junction is passive if non-amplifying rounding is
applied to
.) Since there are no additions following the transformer
multiplies, double-precision adders are not needed. However, precision and
a half is needed in the junction adders to accommodate the worst-case
increased dynamic range. Since the one-multiply junction is structurally
lossless, the overall junction is passive if non-amplifying rounding is
applied to ![]() ,
, ![]() , and the outgoing wave variables from the
transformer and from the one-multiply junction.
, and the outgoing wave variables from the
transformer and from the one-multiply junction.
In summary, a general means of obtaining passive waveguide junctions is to compute exact results internally, and apply saturation (clipping on overflow) and magnitude truncation (truncation toward zero) to the final outgoing wave variables. Because the Kelly-Lochbaum and one-multiply junctions are structurally lossless, exact intermediate results are obtainable using extended internal precision. For the (four-multiply) normalized scattering junction, a passive rounding rule can be developed based on two sign bits. For the three-multiply normalized scattering junction, it is sufficient to apply magnitude truncation to the transformer coefficients and all outgoing wave variables.
Next Section:
Digital Waveguide Filters
Previous Section:
Alternative Wave Variables








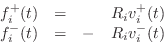
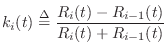
![\includegraphics[scale=0.9]{eps/Fkl}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3611.png)
![\includegraphics[scale=0.9]{eps/Fom}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3616.png)
![\includegraphics[scale=0.9]{eps/scatnlf}](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3623.png)
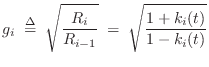
![$\displaystyle \underbrace{\frac{[f^{{+}}_i(t)]^2}{R_i(t)}
+ \frac{[f^{{-}}_{i-1...
...t-T)]^2}{R_{i-1}(t)}
+ \frac{[f^{{-}}_i(t)]^2}{R_i(t)}}_{\mbox{incoming power}}$](http://www.dsprelated.com/josimages_new/pasp/img3656.png)











