
Add a Power Marker to a Power Spectral Density (PSD) Plot
Perhaps we should call most Power Spectral Density (PSD) calculations relative PSD, because usually we don’t have to worry about absolute power levels. However, for cases (e.g., measurements or simulations) where we are concerned with...
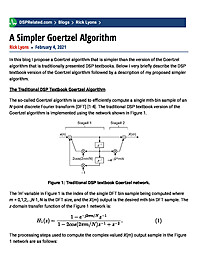
A Simpler Goertzel Algorithm
In this blog I propose a Goertzel algorithm that is simpler than the version of the Goertzel algorithm that is traditionally presented DSP textbooks. Below I very briefly describe the DSP textbook version of the Goertzel algorithm followed by a...
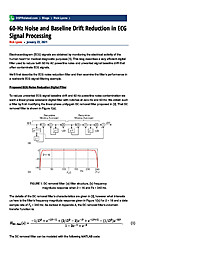
60-Hz Noise and Baseline Drift Reduction in ECG Signal Processing
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals are obtained by monitoring the electrical activity of the human heart for medical diagnostic purposes [1]. This blog describes a very efficient digital filter used to reduce both 60 Hz AC powerline noise and...

Find Aliased ADC or DAC Harmonics (with animation)
When a sinewave is applied to a data converter (ADC or DAC), device nonlinearities produce harmonics. If a harmonic frequency is greater than the Nyquist frequency, the harmonic appears as an alias. In this case, it is not at once...

Adaptive Beamforming is like Squeezing a Water Balloon
Adaptive beamforming was first developed in the 1960s for radar and sonar applications. The main idea is that signals can be captured using multiple sensors and the sensor outputs can be combined to enhance the signals propagating from...
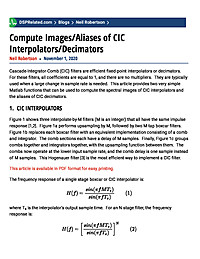
Compute Images/Aliases of CIC Interpolators/Decimators
Cascade-Integrator-Comb (CIC) filters are efficient fixed-point interpolators or decimators. For these filters, all coefficients are equal to 1, and there are no multipliers. They are typically used when a large change in sample...

Exploring Human Hearing Range
Human Hearing Range In this post, I'll look at an interesting aspect of Audacity – using it to explore the threshold of human hearing. In my book Digital Signal Processing: A Gentle Introduction with Audio Examples, I go into this topic...

The Zeroing Sine Family of Window Functions
Introduction This is an article to hopefully give a better understanding of the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) by introducing a class of well behaved window functions that the author believes to be previously unrecognized. The definition...
Design Square-Root Nyquist Filters
In his book on multirate signal processing, harris presents a nifty technique for designing square-root Nyquist FIR filters with good stopband attenuation [1]. In this post, I describe the method and provide a Matlab function for designing the filters. You can find a Matlab function by harris for designing the filters at [2].

Make Hardware Great Again
By now you're aware of the collective angst in the US about 5G. Why is the US not a leader in 5G ? Could that also happen -- indeed, is it happening -- in AI ? If we lead in other areas, why not 5G ? What makes it so hard ? This...

Delay estimation by FFT
Given x=sig(t) and y=ref(t), returns [c, ref(t+delta), delta)] = fitSignal(y, x);:Estimates and corrects delay and scaling factor between two signals Code snippet This article relates to the Matlab / Octave code snippet: Delay estimation with...
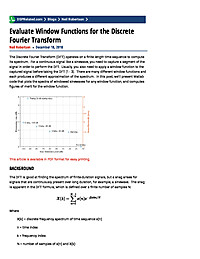
Evaluate Window Functions for the Discrete Fourier Transform
The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) operates on a finite length time sequence to compute its spectrum. For a continuous signal like a sinewave, you need to capture a segment of the signal in order to perform the DFT. Usually, you...
Coupled-Form 2nd-Order IIR Resonators: A Contradiction Resolved
This blog clarifies how to obtain and interpret the z-domain transfer function of the coupled-form 2nd-order IIR resonator. The coupled-form 2nd-order IIR resonator was developed to overcome a shortcoming in the standard 2nd-order IIR resonator....

Add the Hilbert Transformer to Your DSP Toolkit, Part 2
In this part, I’ll show how to design a Hilbert Transformer using the coefficients of a half-band filter as a starting point, which turns out to be remarkably simple. I’ll also show how a half-band filter can be synthesized using the...

Modeling Anti-Alias Filters
Digitizing a signal using an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) usually requires an anti-alias filter, as shown in Figure 1a. In this post, we’ll develop models of lowpass Butterworth and Chebyshev anti-alias filters, and compute the time...

60-Hz Noise and Baseline Drift Reduction in ECG Signal Processing
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signals are obtained by monitoring the electrical activity of the human heart for medical diagnostic purposes [1]. This blog describes a very efficient digital filter used to reduce both 60 Hz AC powerline noise and...

Music/Audio Signal Processing
Greetings,This is my blog from the point of view of a music/audio DSP research engineer / educator. It is informal and largely nontechnical because nearly everything I have to say about signal processing is (or will be) somewhere in my four-book...

Frequency Dependence in Free Space Propagation
IntroductionIt seems to be fairly common knowledge, even among practicing professionals, that the efficiency of propagation of wireless signals is frequency dependent. Generally it is believed that lower frequencies are desirable since pathloss...
Project Report : Digital Filter Blocks in MyHDL and their integration in pyFDA
The Google Summer of Code 2018 is now in its final stages, and I’d like to take a moment to look back at what goals were accomplished, what remains to be completed and what I have learnt. The project overview was discussed in the previous blog...



















