
Off-Topic: A Fluidic Model of the Universe
Introduction This article is a followup to my previous article "Off Topic: Refraction in a Varying Medium"[1]. Many of the concepts should be quite familiar and of interest to the readership of this site. In the "Speculations" section of my...

Learn About Transmission Lines Using a Discrete-Time Model
We don’t often think about signal transmission lines, but we use them every day. Familiar examples are coaxial cable, Ethernet cable, and Universal Serial Bus (USB). Like it or not, high-speed clock and signal traces on...
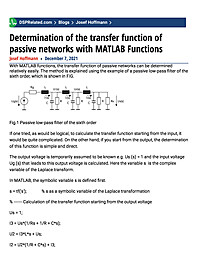
Determination of the transfer function of passive networks with MATLAB Functions
With MATLAB functions, the transfer function of passive networks can be determined relatively easily. The method is explained using the example of a passive low-pass filter of the sixth order, which is shown in FIG.Fig.1 Passive low-pass filter...

A DSP Quiz Question
Here's a DSP Quiz Question that I hope you find mildly interestingBACKGROUNDDue to the periodic natures an N-point discrete Fourier transform (DFT) sequence and that sequence’s inverse DFT, it is occasionally reasonable to graphically plot...

The Discrete Fourier Transform and the Need for Window Functions
The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is used to find the frequency spectrum of a discrete-time signal. A computationally efficient version called the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is normally used to calculate the DFT. But, as many...

Modeling Anti-Alias Filters
Digitizing a signal using an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) usually requires an anti-alias filter, as shown in Figure 1a. In this post, we’ll develop models of lowpass Butterworth and Chebyshev anti-alias filters, and compute the time...

Simulink-Simulation of SSB demodulation
Simulink-Simulation of SSB demodulation or modulation from the article “Understanding the ‘Phasing Method’ of Single Sideband Demodulation” by Richard Lyons Josef Hoffmann The article “Understanding the ‘Phasing Method’ of Single...

Setting Carrier to Noise Ratio in Simulations
When simulating digital receivers, we often want to check performance with added Gaussian noise. In this article, I’ll derive the simple equations for the rms noise level needed to produce a desired carrier to noise ratio (CNR or...

Update to a Narrow Bandpass Filter in Octave or Matlab
Following my earlier blog post (June 2020) featuring a Narrow Bandpass Filter, I’ve had some useful feedback and suggestions. This has inspired me to come up with an updated version, incorporating the following changes compared to the earlier...
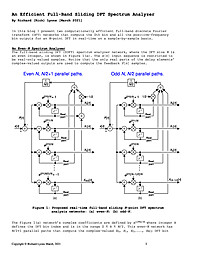
An Efficient Full-Band Sliding DFT Spectrum Analyzer
In this blog I present two computationally efficient full-band discrete Fourier transform (DFT) networks that compute the 0th bin and all the positive-frequency bin outputs for an N-point DFT in real-time on a sample-by-sample basis. An Even-N...
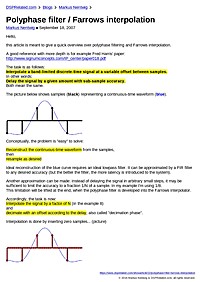
Polyphase filter / Farrows interpolation
Hello, this article is meant to give a quick overview over polyphase filtering and Farrows interpolation. A good reference with more depth is for example Fred Harris' paper: http://www.signumconcepts.com/IP_center/paper018.pdf The task is as...

Add the Hilbert Transformer to Your DSP Toolkit, Part 1
In some previous articles, I made use of the Hilbert transformer, but did not explain its theory in any detail. In this article, I’ll dig a little deeper into how the Hilbert Transformer works. Understanding the Hilbert Transformer...

The Discrete Fourier Transform and the Need for Window Functions
The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is used to find the frequency spectrum of a discrete-time signal. A computationally efficient version called the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is normally used to calculate the DFT. But, as many...

Simulink-Simulation of SSB demodulation
Simulink-Simulation of SSB demodulation or modulation from the article “Understanding the ‘Phasing Method’ of Single Sideband Demodulation” by Richard Lyons Josef Hoffmann The article “Understanding the ‘Phasing Method’ of Single...
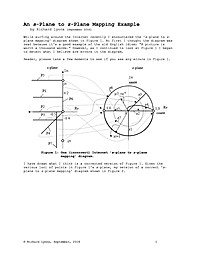
An s-Plane to z-Plane Mapping Example
While surfing around the Internet recently I encountered the 's-plane to z-plane mapping' diagram shown in Figure 1. At first I thought the diagram was neat because it's a good example of the old English idiom: "A picture is worth a thousand...

Digital PLL’s, Part 3 – Phase Lock an NCO to an External Clock
Sometimes you may need to phase-lock a numerically controlled oscillator (NCO) to an external clock that is not related to the system clocks of your ASIC or FPGA. This situation is shown in Figure 1. Assuming your system has an...

The Power Spectrum
Often, when calculating the spectrum of a sampled signal, we are interested in relative powers, and we don't care about the absolute accuracy of the y axis. However, when the sampled signal represents an analog signal, we sometimes need an accurate picture of the analog signal's power in the frequency domain. This post shows how to calculate an accurate power spectrum.
Evaluate Window Functions for the Discrete Fourier Transform
The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) operates on a finite length time sequence to compute its spectrum. For a continuous signal like a sinewave, you need to capture a segment of the signal in order to perform the DFT. Usually, you...

How to Find a Fast Floating-Point atan2 Approximation
Context Over a short period of time, I came across nearly identical approximations of the two parameter arctangent function, atan2, developed by different companies, in different countries, and even in different decades. Fascinated...

Second Order Discrete-Time System Demonstration
Discrete-time systems are remarkable: the time response can be computed from mere difference equations, and the coefficients ai, bi of these equations are also the coefficients of H(z). Here, I try to illustrate this remarkableness by converting a continuous-time second-order system to an approximately equivalent discrete-time system. With a discrete-time model, we can then easily compute the time response to any input. But note that the goal here is as much to understand the discrete-time model as it is to find the response.


















