
Implementation of a Tx/Rx OFDM System in a FPGA
The aim of this project consists in the FPGA design and implementation of a transmitter and receiver (Tx/Rx) multicarrier system such the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). This Tx/Rx OFDM subsystem is capable to deal with with different M-QAM modulations and is implemented in a digital signal processor (DSP-FPGA). The implementation of the Tx/Rx subsystem has been carried out in a FPGA using both System Generator visual programming running over Matlab/Simulink, and the Xilinx ISE program which uses VHDL language. This project is divided into four chapters, each one with a concrete objective. The first chapter is a brief introduction to the digital signal processor used, a field-programmable gate array (FPGA), and to the VHDL programming language. The second chapter is an overview on OFDM, its main advantages and disadvantages in front of previous systems, and a brief description of the different blocks composing the OFDM system. Chapter three provides the implementation details for each of these blocks, and also there is a brief explanation on the theory behind each of the OFDM blocks to provide a better comprehension on its implementation. The fourth chapter is focused, on the one hand, in showing the results of the Matlab/Simulink simulations for the different simulation schemes used and, on the other hand, to show the experimental results obtained using the FPGA to generate the OFDM signal at baseband and then upconverted at the frequency of 3,5 GHz. Finally the conclusions regarding the whole Tx/Rx design and implementation of the OFDM subsystem are given.

Real Time Implementation of Multi-Level Perfect Signal Reconstruction Filter Bank
Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) is an efficient tool for signal and image processing applications which has been utilized for perfect signal reconstruction. In this paper, twenty seven optimum combinations of three different wavelet filter types, three different filter reconstruction levels and three different kinds of signal for multi-level perfect reconstruction filter bank were implemented in MATLAB/Simulink. All the filters for different wavelet types were designed using Filter Design Analysis (FDA) and Wavelet toolbox. Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) was calculated for each combination. Combination with best SNR was then implemented on TMS320C6713 DSP kit. Real time testing of perfect reconstruction on DSP kit was then carried out by two different methods. Experimental results accede with theory and simulations.

A Multimedia DSP processor design
This Master Thesis presents the design of the core of a fixed point general purpose multimedia DSP processor (MDSP) and its instruction set. This processor employs parallel processing techniques and specialized addressing models to speed up the processing of multimedia applications. The MDSP has a dual MAC structure with one enhanced MAC that provides a SIMD, Single Instruction Multiple Data, unit consisting of four parallel data paths that are optimized for accelerating multimedia applications. The SIMD unit performs four multimedia-oriented 16-bit operations every clock cycle. This accelerates computationally intensive procedures such as video and audio decoding. The MDSP uses a memory bank of four memories to provide multiple accesses of source data each clock cycle.

Implementation of Uncoordinated Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum using Software Defined Radios
One of the major threats to wireless communications is jamming. Many anti-jamming techniques have been presented in the past. However most of them are based on the precondition that the communicating devices have a pre-shared secret that can be used to synchronize the anti-jamming scheme. E.g. for frequency hopping the secret could be used to derive the hopping sequence and for direct sequence spread spectrum the secret is used to derive the spreading codes. But how can the devices bootstrap a jamming-resistant communication without having a pre-shared secret? Christina Popper and Mario Strasser propose as scheme for Uncoordinated Frequency Hopping (UFH) and Uncoordinated Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (UDSSS) in their papers [1] and [2] respectively. The goal of my project was an implementation of Uncoordinated Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (UDSSS) using Software De ned Radios. The First version should serve as an easy to use and extendable proof of conceptfor the proposed scheme.

Algorithms and tools for automatic generation of DSP hardware structures
The increased complexity of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) algorithms demands for the development of more complex and more efficient hardware structures. The work presented herein describes the core components for the development of a tool capable of automatic generation of efficient hardware structures, therefore facilitating developers work. It comprises algorithms and techniques for i) balancing the paths in a graph, ii) scheduling of operations to functional units, iii) allocating registers and iv) generating the VHDL code. Results show that the developed techniques are capable of generating the hardware structure of typical DSP algorithms represented in data-flow graphs with over 2,000 nodes in around 200 ms, scaling to 80,000 nodes in about 214 s. Within the developed techniques, solving the scheduling problem is one of the most complex tasks: it is a NP-complete problem and directly influences the number of functional units and registers required. Therefore, experimental analysis was made on scheduling algorithms for time-constrained problems. Results show that simple list-based algorithms are more efficient in large problems than more complex algorithms: they run faster and tend to require less functional units.

Music Signal Processing
Chapter 12 of the book "Multimedia Signal Processing: Theory and Applications in Speech, Music and Communications" - Musical Instruments - A Review of Basic Physics of Sound - Music Signal Features and Models - Ear: Hearing of Sounds - Psychoacoustics of Hearing - Music Compression - High Quality Music Coding: MPEG - Stereo Music - Music Recognition

High speed data collection with Blackfin DSP
This report covers a master thesis in embedded systems, the goal of which was to investigate the high speed data collection capabilities with a Blackfin DSP. Basic theory about sampling and noise is covered briefly from a practical point of view. The theory is intended to be useful for those diving into a ADC datasheet for the first time. After an investigation of the delimiting factors, suitable components were selected and a prototype ADC PCB was designed from scratch. The goal is to design a general low noise data collecting unit compatible with the Blackfin DSP. Finally simple DSP software is designed to prove that DSP can handle such a high datastream.Testing the ADC card with the target Blackfin platform indicates thatthe analog parts indeed works. An analog bandwidth of over 10MHz ismeasured at a resolution exceeding 10 bits with respect to noise. The digital parts intended to interleave the two channels digital streams into one Blackfin unit did not work as intended. Only one channel is supported as of now. The report contains suggestions for future work in this area.

Active Noise Control of a Forest Machine Cabin
Today, a high noise level is considered a problem in many working environments. The main reason is that it contributes to stress and fatigue. Traditional methods using passive noise control is only practicable for high frequencies. As a complement to passive noise control, active noise control (ANC) can be used to reduce low frequency noise. The main idea of ANC is to use destructive interference of waves to cancel disturbing noises. The purpose of this thesis is to design and implement an ANC system in the driver's cabin of a Valmet 890 forest machine. The engine boom is one of the most disturbing noises and therefore the main subjective for the ANC system to suppress. The ANC system is implemented on a Texas Instrument DSP development starter kit. Different FxLMS algorithms are evaluated with feedback and feedforward configurations. The results indicate that an ANC system significantly reduces the sound pressure level (SPL) in the cabin. Best performance of the evaluated systems is achieved for the feedforward FxLMS system. For a commonly used engine speed of 1500 rpm, the SPL is reduced with 17 dB. The results show fast enough convergence and global suppression of low frequency noise.

Evaluation of a Floating Point Acoustic Echo Canceller Implementation
This master thesis consists of implementation and evaluation of an AEC, Acoustic Echo Canceller, algorithm in a floating-point architecture. The most important question this thesis will try to answer is to determine benefits or drawbacks of using a floating-point architecture, relative a fixed-point architecture, to do AEC. In a telephony system there is two common forms of echo, line echo and acoustic echo. Acoustic echo is introduced by sound emanating from a loudspeaker, e.g. in a handsfree or speakerphone, being picked up by a microphone and then sent back to the source. The problem with this feedback is that the far-end speaker will hear one, or multiple, time-delayed version(s) of her own speech. This time-delayed version of speech is usually perceived as both confusing and annoying unless removed by the use of AEC. In this master thesis the performance of a floating-point version of a normalized least-mean-square AEC algorithm was evaluated in an environment designed and implemented to approximate live telephony calls. An instruction-set simulator and assembler available at the initiation of this master thesis were extended to enable; zero-overhead loops, modular addressing, post-increment of registers and register-write forwarding. With these improvements a bit-true assembly version was implemented capable of real-time AEC requiring 15 million instructions per second. A solution using as few as eight mantissa bits, in an external format used when storing data in memory, was found to have an insignificant effect on the selected AEC implementation’s performance. Due to the relatively low memory requirement of the selected AEC algorithm, the use of a small external format has a minor effect on the required memory size. In total this indicates that the possible reduction of the memory requirement and related energy consumption, does not justify the added complexity and energy consumption of using a floating-point architecture for the selected algorithm. Use of a floating-point format can still be advantageous in speech-related signal processing when the introduced time delay by a subband, or a similar frequency domain, solution is unacceptable. Speech algorithms that have high memory use and small introduced delay requirements are a good candidate for a floating-point digital signal processor architecture.

Decoding Ogg Vorbis Audio with The C6416 DSP, using a custom made MDCT core on FPGA
Ogg Vorbis is a fairly new and growing audio format, often used for online distribution of music and internet radio stations for streaming audio. It is considered to be better than MP3 in both quality and compression and in the same league as for example AAC. In contrast with many other formats, like MP3 and AAC, Ogg Vorbis is patent and royalty free. The purpose of this thesis project was to investigate how the C6416 DSP processor and a Stratix II FPGA could be connected to each other and work together as co-processors and using an Ogg Vorbis decoder as implementation example. A fixed-point decoder called Tremor (developed by Xiph.Org the creator of the Vorbis I specification), has been ported to the DSP processor and an Ogg Vorbis player has been developed. Tremor was profiled before performing the software / hardware partitioning to decide what parts of the source code of Tremor that should be implemented in the FPGA to off-load and accelerate the DSP.

DSP Memory Management in a Third Generation High Performance Base Station
Most of the tasks in a mobile cellular network base station are performed with programmable digital signal processors. Their memory spaces and management features are very limited. The buffering requirements in the base station can have large instantaneous variations during the simultaneous transmission of burst' data on multiple channels to multiple users. In particular the high bit-rates of the Wideband Code Division Multiple Access data transfer evolution High Speed Downlink Packet Access create very high demands for buffering. The fragmentation of the buffer memory is a threat. It causes a gradual decrease in performance, which is critical in a long running process like the base station. The amount of fragmentation is different with different memory management methods. In this work the features and applicability of different memory management methods for signal processors used in the base stations of third generation cellular networks have been studied. Software based memory management includes a high amount of conditional branches. The signal processor, which is optimized for highly parallel sequential computing, executes conditional branches very badly when compared to microcontrollers and general-purpose processors. The memory management methods are first studied in theory and then experimentally. In the experiments two different memory management methods were analyzed. The memory managers were loaded with a synthetic workload program that simulates multi-user high bit-rate data transmissions in the base station. The performances of the memory managers were measured in terms of fragmentation, execution time and memory utilization. The experiments confirmed the information gained from the theoretical studies that different memory management methods are usually optimized for a certain feature. The experiments showed that a simple method is fast to execute and works well with small and intermediate loads. When the load is increased the performance decreases. The second, more complex, measured method was found to require more computing, but to be capable of using the memory space assigned to it more effectively.

An Advanced Signal Processing Toolkit for Java applications
The aim of this study is to examine the capability, performance, and relevance of a signal processing toolkit in Java, a programming language for Web-based applications. Due to the simplicity, ease and application use of the toolkit and with the advanced Internet technologies such as Remote Method Invocation (RMI), a spectral estimation applet has been created in the Java environment. This toolkit also provides an interactive and visual approach in understanding the various theoretical concepts of spectral estimation and shows the need to create more application applets to better understand the various concepts of signal and image processing. This study also focuses on creating a Java toolkit for embedded systems, such as Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), embedded Java board, and supporting integer precision, and utilizing COordinate Rotation DIgital Computer (CORDIC) algorithm, both aimed to provide good performance in resource-limited environments. The results show a feasibility and necessity of developing a standardized Application Programming Interface (API) for the fixed-point signal processing library.

A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems
In 1960, R.E. Kalman published his famous paper describing a recursive solution to the discrete-data linear filtering problem. Since that time, due in large part to advances in digital computing, the Kalman filter has been the subject of extensive research and application, particularly in the area of autonomous or assisted navigation.

Cascaded Integrator-Comb (CIC) Filter Introduction
In the classic paper, "An Economical Class of Digital Filters for Decimation and Interpolation", Hogenauer introduced an important class of digital filters called "Cascaded Integrator-Comb", or "CIC" for short (also sometimes called "Hogenauer filters"). Here, Matthew Donadio provides a more gentle introduction to the subject of CIC filters, geared specifically to the needs of practicing DSP designers.

The DFT of Finite-Length Time-Reversed Sequences
Recently I've been reading papers on underwater acoustic communications systems and this caused me to investigate the frequency-domain effects of time-reversal of time-domain sequences. I created this article because there is so little coverage of this topic in the literature of DSP.
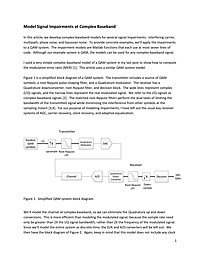
Model Signal Impairments at Complex Baseband
In this article, we develop complex-baseband models for several signal impairments: interfering carrier, multipath, phase noise, and Gaussian noise. To provide concrete examples, we'll apply the impairments to a QAM system. The impairment models are Matlab functions that each use at most seven lines of code. Although our example system is QAM, the models can be used for any complex-baseband signal.

Algorithms, Architectures, and Applications for Compressive Video Sensing
The design of conventional sensors is based primarily on the Shannon-Nyquist sampling theorem, which states that a signal of bandwidth W Hz is fully determined by its discrete-time samples provided the sampling rate exceeds 2W samples per second. For discrete-time signals, the Shannon-Nyquist theorem has a very simple interpretation: the number of data samples must be at least as large as the dimensionality of the signal being sampled and recovered. This important result enables signal processing in the discrete-time domain without any loss of information. However, in an increasing number of applications, the Shannon-Nyquist sampling theorem dictates an unnecessary and often prohibitively high sampling rate. (See Box 1 for a derivation of the Nyquist rate of a time-varying scene.) As a motivating example, the high resolution of the image sensor hardware in modern cameras reflects the large amount of data sensed to capture an image. A 10-megapixel camera, in effect, takes 10 million measurements of the scene. Yet, almost immediately after acquisition, redundancies in the image are exploited to compress the acquired data significantly, often at compression ratios of 100:1 for visualization and even higher for detection and classification tasks. This example suggests immense wastage in the overall design of conventional cameras.

Decimator Image Response
This article presents a way to compute and plot the image response of a decimator. I'm defining the image response as the unwanted spectrum of the impulse response after downsampling, relative to the desired passband response.

Filter a Rectangular Pulse with no Ringing
To filter a rectangular pulse without any ringing, there is only one requirement on the filter coefficients: they must all be positive. However, if we want the leading and trailing edge of the pulse to be symmetrical, then the coefficients must be symmetrical. What we are describing is basically a window function.

Implementing Simultaneous Digital Differentiation, Hilbert Transformation, and Half-Band Filtering
Recently I've been thinking about digital differentiator and Hilbert transformer implementations and I've developed a processing scheme that may be of interest to the readers here on dsprelated.com.


















